108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

检测参与肝细胞癌发展的癌症相关成纤维细胞的新型 12-标志物组
Authors Zou B, Liu X, Gong Y, Cai C, Li P, Xing S, Pokhrel B, Zhang B, Li J
Received 2 June 2018
Accepted for publication 20 August 2018
Published 5 November 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 5303—5311
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S176152
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Background/Aim: Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are important factors in the
progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). But the characterization of
these cells remains incomplete. This study aims to identify a panel of markers
for CAFs that are associated with HCC progression.
Materials and
methods: The sequencing data and
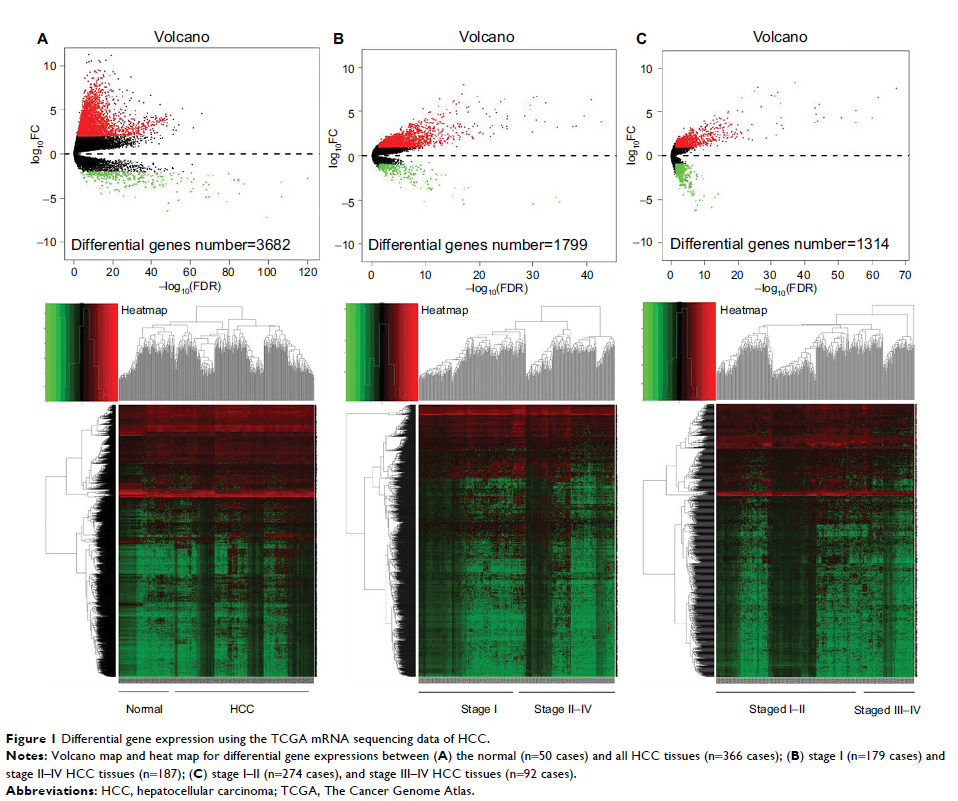
clinicopathological characteristics of 366 patients were obtained from the
Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database (366 HCC tissues and there were 50/366
cases with corresponding normal liver tissues). In vitro validation of the
markers was performed by quantitative real-time PCR using the hepatic stellate
cell line LX2 induced by the HCC cell line Huh7. The activation of LX2 was
confirmed by α-smooth muscle actin and fibroblast activation protein, using
quantitative real-time PCR and immunofluorescence staining. In vivo detections
of the 12 markers were done in 40 tissue samples (30 HCC and 10 normal).
Results: We successfully identified 12 CAF markers from TCGA data: FGF5,
CXCL5, IGFL2, MMP1, ADAM32, ADAM18, IGFL1, FGF8, FGF17, FGF19, FGF4, and FGF23.
The 12-marker panel was associated with the pathological and clinical
progressions of HCC. All 12 markers were upregulated in vitro. In vivo
expressions of these markers were paralleled with those in TCGA data.
Conclusion: A 12-marker panel of CAFs in HCC is identified, which is associated with
both pathological and clinical progressions of cancer.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, cancer-associated fibroblasts, CAFs marker
panel, TCGA database analysis, transcriptome profiling