108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

具有耐药质粒的临床铅黄肠球菌的分子特征和比较基因组学分析
Authors Yin M, Jiang Y, Qian C, Wu F, Ying Y, Wu C, Li P, Ying J, Li K, Xu T, Bao Q, Sun C
Received 14 July 2018
Accepted for publication 3 September 2018
Published 5 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2159—2167
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S180254
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eric Nulens
Purpose: The aim of this work was to investigate the molecular
characterization of a clinical Enterococcus casseliflavus strain
with a resistance plasmid.
Materials and
methods: En. casseliflavus EC369 was
isolated from a patient in a hospital in southern China. The minimum inhibitory
concentration was found by means of the agar dilution method to determine the
antimicrobial susceptibilities of the strains. Whole-genome sequencing and
comparative genomics analysis were performed to analyze the mechanism of
antibiotic resistance and the horizontal gene transfer of the resistance
gene-related mobile genetic elements.
Results: En. casseliflavus EC369 showed
resistance to erythromycin, kanamycin, and streptomycin, but was susceptible to
vancomycin, ampicillin, and streptothricin and other antimicrobials. There were
six resistance genes (aph3′ , ant6 , bla , sat4 , and two ermBs ) carried by a transposon
identified on the plasmid pEC369 and a complete resistance gene cluster of
vancomycin and a tet (M ) gene encoded on the chromosome.
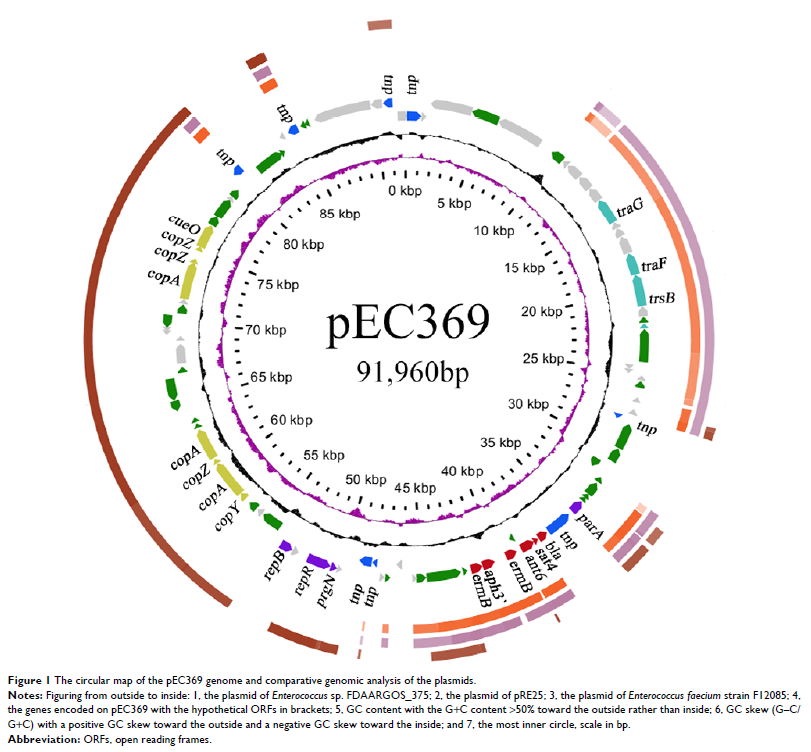
This is the first complete plasmid sequence reported in clinically
isolated En. casseliflavus . The plasmid with
the greatest sequence identity with pEC369 was the plasmid of Enterococcus sp.
FDAARGOS_375, followed by the plasmids of Enterococcus
faecium strains F12085 and pRE25, whereas the sequence with
the greatest identity to the resistance genes carrying a transposon of pEC369
was on the chromosome of Staphylococcus aureus strain
GD1677.
Conclusion: The resistance profiles of En. casseliflavus EC369 might
contribute to the resistance genes encoded on the plasmid. The fact that the
most similar sequence to the transposon carrying resistance genes of pEC369 was
encoded in the chromosome of a S. aureus strain provides
insights into the mechanism of dissemination of multidrug resistance between
bacteria of different species or genera through horizontal gene transfer.
Keywords: Enterococcus casseliflavus ,
antimicrobial resistance, transposon, molecular characteristics, comparative
genomics analysis