108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

加载逆向蛋白质底物的间充质干细胞移植可抑制急性心肌梗塞小鼠的心肌重塑
Authors Lu W, Ji J, Ma G, Dai Q, Chen L, Zuo P, Zhao Y
Received 26 June 2018
Accepted for publication 1 October 2018
Published 2 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7033—7046
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S178270
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: The two-dimensional incubation method is now the most commonly method
for mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) production. however, gene expression and
secretion of growth factors are relatively low; thus, the transplanted cells
cannot be effectively utilized for potential clinical applications after acute
myocardial infarction (AMI).
Objectives: We aimed to investigate whether our newly made
substrates of inverse opal with specific surface microstructures for MSC
culturing can increase the viability of the cells and can contributes to
decreased myocardial remodeling after transplanted to AMI mice.
Methods: The inverse opal structure is fabricated by the
convenient bottom-up approach of the self-assembly of colloidal nanoparticles.
Mouse-derived MSCs were then cultured on the substrates when expanded at
different times to investigate the cell growth status including morphology.
Then the inverse opal substrates loaded MSCs were transplanted to AMI mice,
cardiomyocyte apoptosis and LV remodeling were further compared. To explore the
possible mechanisms of curation, the secretions and viability of MSCs on
substrates were determined using mice ELISA kits and JC-1 mitochondrial
membrane potential assay kits respectively at normal and hypoxic
conditions.
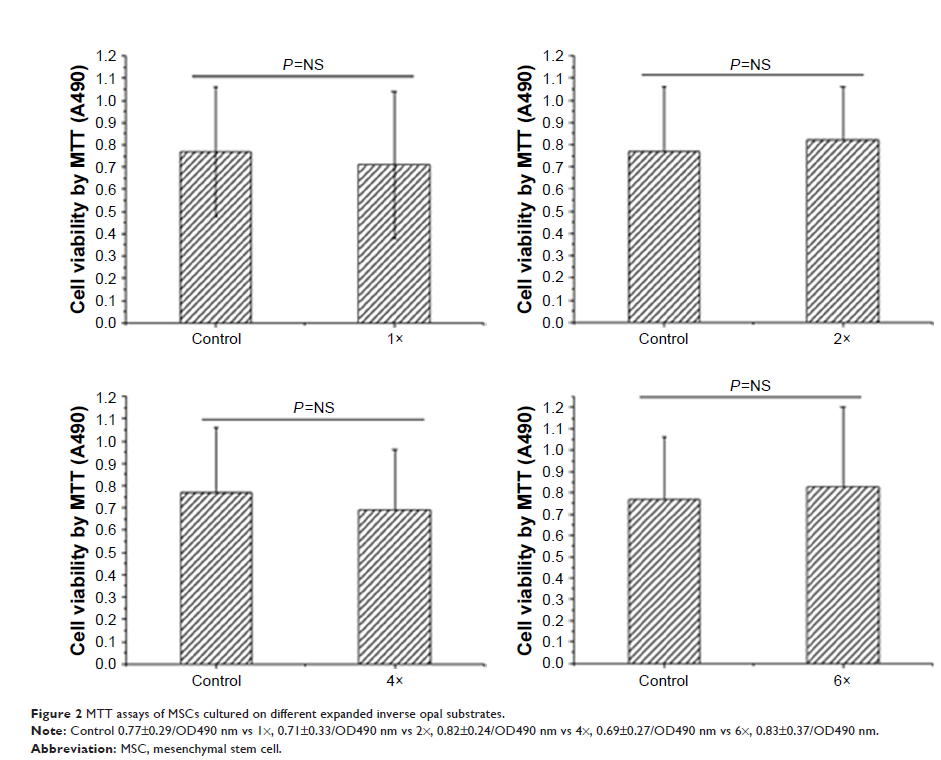
Results: 6 times expanded inverse opals allowed greatly
the orderly growth of MSCs as compared to four (34% ± 10.6%) and two (20%±7.2%)
times expanded as well as unexpanded (13%±4.1%) (P <0.001).
Nearly 90% of MSCs showed orientation angle intervals of less than 30° when at
the 6X expanded (89.6%±25%) compared to the percent of cells with 30°–60°
(8.7%±2.6%) or ≥60° (1.7%±1.0%) orientation angle (P <0.001).
After inverse opal loaded MSCs transplanted to AMI mice, greatly decreased
apoptosis of cardiomyocytes (20.45%±8.64% vs.39.63%±11.71%, P <0.001) and infarction area
(5.87±2.18 mm2 vs 9.31±3.11mm2, P <0.001) were identified.
In the end, the viability of inverse opal loaded MSCs determined by membrane
potential (P <0.001) and the secretion of
growth factors including VEGF-α, SDF-1 and Ang-1 (P <0.001)
were both confirmed significantly higher than that of the conventional culture
in petri dish.
Conclusion: The structure of inverse opal can not only
adjust the arrangement of MSCs but also contribute to its orientated growth.
Inverse opal loaded MSCs transplantation extremely curbed myocardial
remodeling, the underlying mechanisms might be the high viability and extremely
higher secretions of growth factors of MSCs as devoted by this method.
Keywords: MSCs, inverse
opal, AMI