109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

铜离子 (Cu2+)-RGDFRGDS: 探索纳米颗粒在抗血栓治疗中的机理和高功效
Authors Wu J, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhao M, Zhang X, Gui L, Zhao S, Zhu H, Zhao J, Peng S
Published Date April 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 2925—2938
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S76691
Received 30 October 2014, Accepted 19 January 2015, Published 15 April 2015
Abstract: Thrombosis
disease has been the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. In the
discovery of antithrombotic agents, three complexes of Cu2+ and
repetitive arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) sequences,
Cu(II)-Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (Cu[II]-4a),
Cu(II)-Arg-Gly-Asp-Val-Arg-Gly-Asp-Val (Cu[II]-4b), and
Cu(II)-Arg-Gly-Asp-Phe-Arg-Gly-Asp-Phe (Cu[II]-4c), were previously reported,
of which Cu(II)-4a and Cu(II)-4c possessed the highest in vitro and in vivo
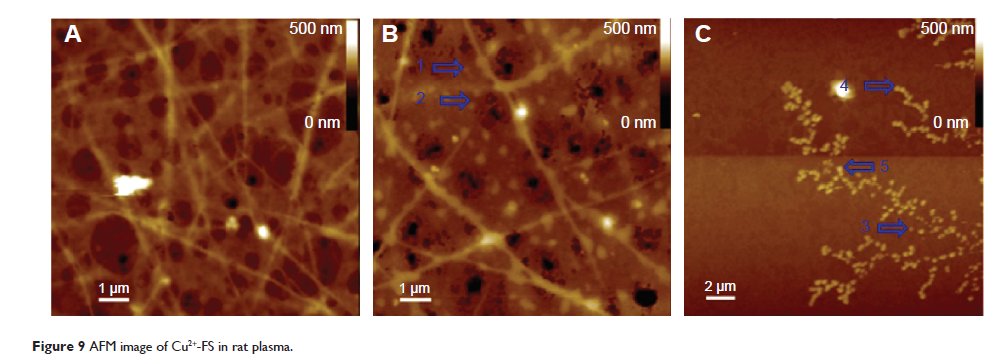
activity, respectively. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images
visualized that Cu(II)-4a and Cu(II)-4c formed nanoaggregates and
nanoparticles, respectively. However, the details of the formation of the
nanospecies complexes and of the mechanism for inhibiting thrombosis remain to be
clarified. For this purpose, this study designed a novel complex of Cu(II) and
the RGD octapeptide, Arg-Gly-Asp-Phe-Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (RGDFRGDS), consisting of
Arg-Gly-Asp-Phe of Cu(II)-4c and Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser of Cu(II)-4a, to colligate
their biological and nanostructural benefits. In contrast with Cu(II)-4a, -4b,
and -4c, Cu(II)-RGDFRGDS (Cu2+-FS) had high antiplatelet and
antithrombotic activities, with the formed nanoparticles having a porous
surface. Additionally, this paper evidenced the dimer had the basic structural
unit of Cu2+-FS in water, theoretically simulated the formation of
Cu2+-FS nanoparticles, and identified that Cu2+-FS
activity in decreasing glycoprotein IIb/IIIa, P-selectin, and IL-8 was
responsible for the antithrombotic action. Finally, adherence onto the surface
and entry into the cytoplasm were considered the steps of a two-step model for
the blocking of platelet activation by Cu2+-FS nanoparticles.
Findings indicated that the antiplatelet aggregation activity of Cu2+-FS
was 10–52 times higher than that of RGDFRGDS, while the effective dose for
antithrombotic action was 5,000 times lower than that of RGDFRGDS.
Keywords: GPIIb/IIIa, IL-8,
TEM, AFM, SEM, nanomedicine