108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MicroRNA-645 通过靶向尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活剂,降低 MDA-MB-231 三阴性乳腺癌细胞的侵袭性生长
Authors Meng D, Lei M, Han Y, Zhao D, Zhang X, Yang Y, Liu R
Received 11 September 2018
Accepted for publication 8 October 2018
Published 2 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 7733—7743
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S187221
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
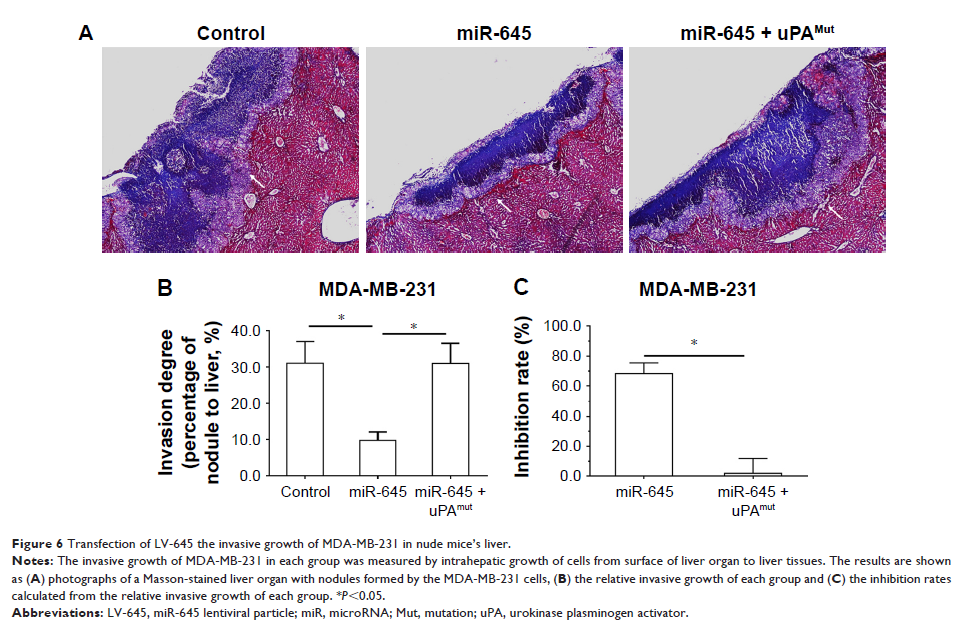
Background: Urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) promotes the in vivo
invasive growth of HCC cells by cleaving and activating matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs) to induce the destruction of the extracellular matrix
of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. The identification of microRNAs
that target uPA and decrease uPA expression would be useful for attenuating the
in vivo invasive growth of TNBC cells.
Materials and
methods: MicroRNA-645 (miR-645) was
identified using an online tool (miRDB) as potentially targeting uPA; miR-645
inhibition of uPA was confirmed by western blot experiments. The effects of
miR-645 on the in vivo invasive growth of TNBC cells were examined using an
intrahepatic tumor model in nude mice, and the miR-645 mechanism of action was
explored with MMP cleaving experiments.
Results: Through virtual screening, we discovered that miR-645 potentially
targeted the uPA 3' untranslated region. This targeting was confirmed by
western blot experiments and miR-645 lentiviral particle (LV-645) transduction
that inhibited uPA expression in MDA-MB-231 TNBC cells. The LV-645 inhibition
of uPA led to the decreased invasive growth of TNBC cells in nude mice. The
mechanism data indicated that the uPA inhibition resulted in a decreased
cleaving of the pro-MMP-9 protein.
Conclusion: Targeting uPA with miR-645 decreased the in vivo invasive growth of TNBC
cells. These results suggest that miR-645 may represent a promising treatment
strategy for TNBC.
Keywords: triple-negative breast cancer, urokinase plasminogen activator,
microRNA, invasive growth