108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用黄果茄提取物合成金纳米粒子及其对鼻咽癌细胞的体外抗癌作用
Authors Zhang P, Wang P, Yan L, Liu L
Received 13 July 2018
Accepted for publication 3 August 2018
Published 1 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7047—7059
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S180138
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC) is one of the subtypes of head and
neck cancers. It occurs rarely, and its prevalence depends mainly on
geographical location. Modern-day research is focused on coupling
nanotechnology and traditional medicine for combating cancers. Gold
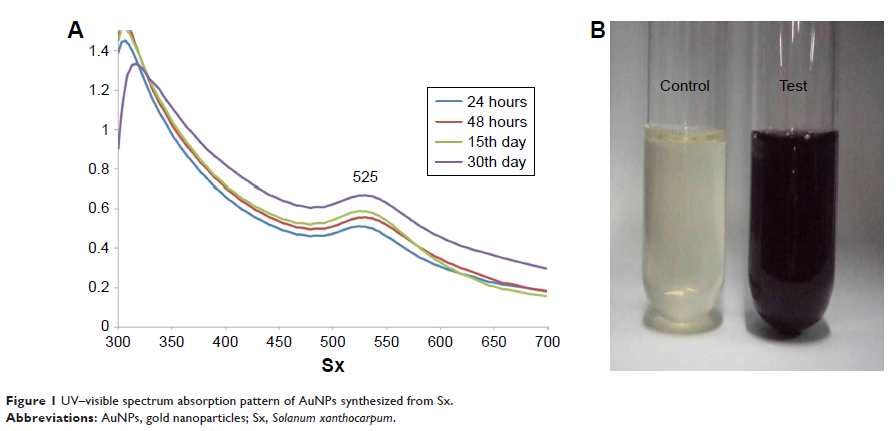
nanoparticles (AuNPs) were synthesized from Solanum
xanthocarpum (Sx) leaf extract using reduction method.
Methods: Characterization of the synthesized AuNPs was done by different
techniques such as ultraviolet–visible spectrum absorption, X-ray diffraction,
dynamic light scattering, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, transmission
electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis.
Results: All the results showed the successful
green synthesis of AuNPs from Sx, which induced apoptosis of C666-1 cell line
(NPC cell line). There was a decline in both cell viability and colony formation
in C666-1 cells upon treatment with Sx-AuNPs. The cell death was proved to be
caused by autophagy and mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic pathway.
Conclusion: Thus, due to their anticancer potential, these nanoparticles
coupled with Sx can be used for in vivo applications and clinical research in
future.
Keywords: Solanum xanthocarpum , gold
nanoparticle, C666-1 cells, ROS, apoptosis