108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

结直肠癌中 PD-L2 表达的临床病理分析
Authors Guo PD, Sun ZW, Lai HJ, Yang J, Wu PP, Guo YD, Sun J
Received 15 June 2018
Accepted for publication 15 August 2018
Published 1 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 7635—7642
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S177329
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: (PD-L2), a ligand of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), is an
inhibitory receptor of T cells and activated B cells. Many studies have focused
on PD-L1, another ligand of PD-1, and the prognostic significance of PD-L1 has
been reported in many tumors. However, the expression of PD-L2 in relation to
clinical outcomes has not been fully investigated in cancer patients.
Patients and
methods: In this study, we investigated the
expression of PD-L2 via immunohistochemistry (IHC) in the pathological
specimens of 348 patients treated for colorectal cancer (CRC).
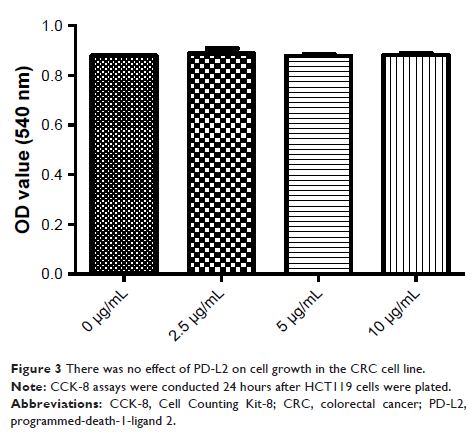
Results: Strong PD-L2 expression was found in the cancer tissues from 41%
of the CRC patients who also had a high TNM stage and carcinoembryonic antigen
(CEA) concentration. We also carried out functional studies in vitro, which
showed that PD-L2 did not influence the growth of the CRC cell line HCT116, but
increased cell invasion.
Conclusion: Collectively, these findings suggest that PD-L2 may be a potential
therapeutic target for CRC.
Keywords: PD-L2, colorectal cancer, migration, therapeutic target