108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

INPPL1 的低表达与乳头状甲状腺癌的明显的临床病理学特征有关
Authors Zhou YL, Zheng C, Chen YT, Chen XM
Received 30 August 2018
Accepted for publication 10 October 2018
Published 1 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 7725—7731
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S185803
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Purpose: To study the relationship between INPPL1 gene
and clinicopathologic characteristics of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC).
Patients and
methods: INPPL1 expression in PTCs was
tested by quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR. The Cancer Genome
Atlas (TCGA) RNA-seq data and our mRNA data were used to analyze and reveal the
relationship between INPPL1 and aggressive clinicopathologic characteristics of
PTC.
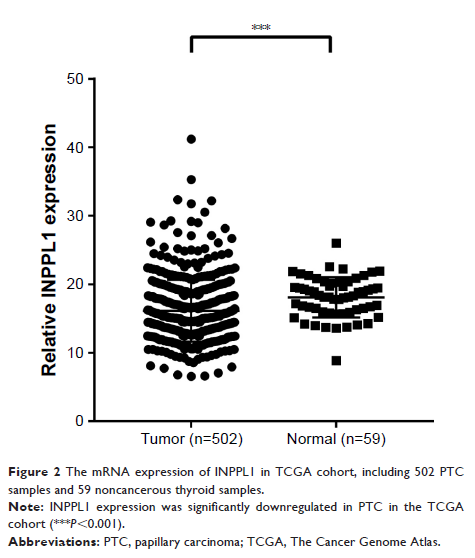
Results: When compared to normal thyroid tissues, INPPL1 was significantly
downregulated in PTC tissues, as revealed by our data and TCGA data. INPPL1
underexpression was remarkably related to aggressive clinicopathologic
characteristics such as lymph node metastasis (LNM), histological type, tumor
size, mulitifocality, and disease stage in TCGA data. Meanwhile, LNM was
confirmed to be associated with underexpression of INPPL1 in our data. In
addition, logistic analysis clearly showed that underexpression of INPPL1 was
an independent factor for LNM in PTC.
Conclusion: INPPL1 may be a novel tumor suppressor gene in PTC, which was
significantly correlated with aggressive clinicopathologic characteristics,
especially LNM.
Keywords: papillary thyroid carcinoma, INPPL1 expression, lymph node
metastasis, The Cancer Genome Atlas