108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ASK1 相互作用蛋白-1 的低表达水平与食管鳞状细胞癌患者的肿瘤血管生成和低生存率相关
Authors Sun D, Chen C, Hu W, Zhong C, Fan L, Song X, Gai Z
Received 24 June 2018
Accepted for publication 12 September 2018
Published 1 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 7699—7707
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S178131
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
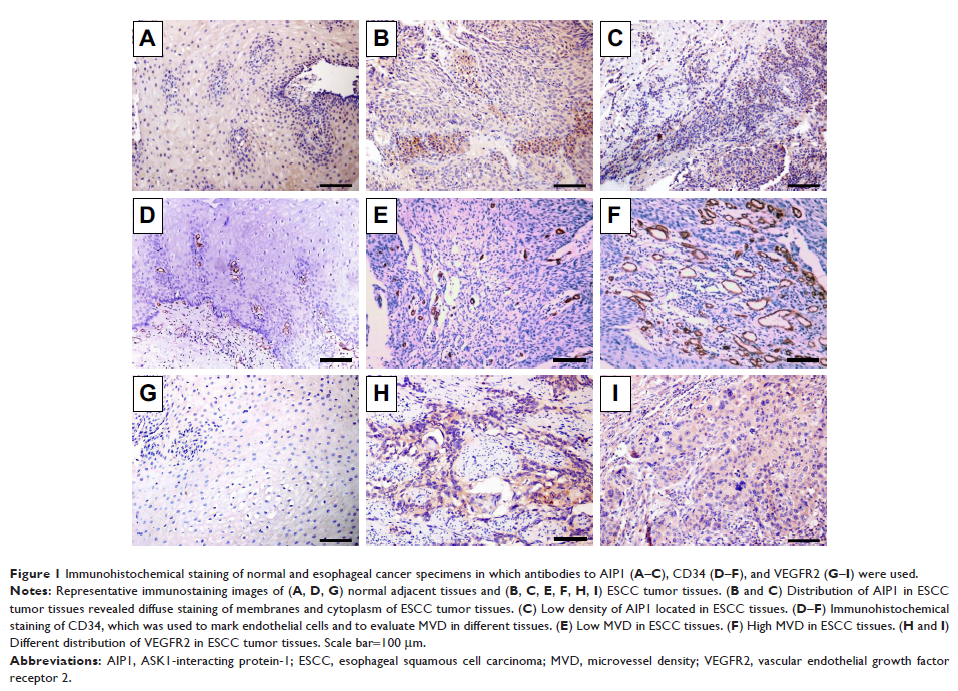
Objective: To investigate the expression of tumor suppressor protein
ASK1-interacting protein-1 (AIP1) in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
(ESCC) and its role in tumor progression, angiogenesis, and prognosis.
Methods: A total of 117 biopsy samples were obtained from ESCC patients. None of
the patients had distant metastasis before surgery, and did not receive
preoperative chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Immunohistochemistry was used to
detect the expression of AIP1 protein and vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor 2 (VEGFR2) in ESCC specimens collected from 117 patients who underwent
esophageal cancer radical surgery. Microvessel density (MVD) was evaluated by
immunohistochemical staining of vascular endothelial CD34. The correlation
between AIP1 protein and clinicopathological characteristics, tumor
angiogenesis, and prognosis was analyzed.
Results: The downregulation of AIP1 protein in esophageal carcinoma tissues was
detected in 63 cases. This downregulation significantly correlated with lymph
node metastasis, clinicopathological staging, and tumor MVD (P <0.05). Survival analysis
showed that ESCC patients with a low expression of AIP1, a high expression of
VEGFR2, and a high level of MVD had a lower 5-year survival rate (P <0.05). Multivariate analysis
confirmed that the downregulation of AIP1 significantly affected patient
survival.
Conclusion: The downregulation of AIP1 correlated with ESCC progression, tumor
angiogenesis, and poor prognosis. AIP1 could be a promising biomarker for
predicting ESCC prognosis and a potential target for anti-angiogenic therapy.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, angiogenesis, ASK1-interacting
protein-1, microvessel density