108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ARHGAP30 通过抑制 Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路抑制肺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Mao X, Tong J
Received 24 May 2018
Accepted for publication 24 July 2018
Published 24 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 7447—7457
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S175255
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Objective: Rho GTPase-activating protein 30 (ARHGAP30), a member of the Rho
GTPase-activating proteins (Rho GAPs) family, plays an important role in the
regulation of cytoskeleton organization and cell adhesion.
Materials and
methods: mRNA and protein expression
was assessed by quantitative real-time PCR and Western blotting, respectively.
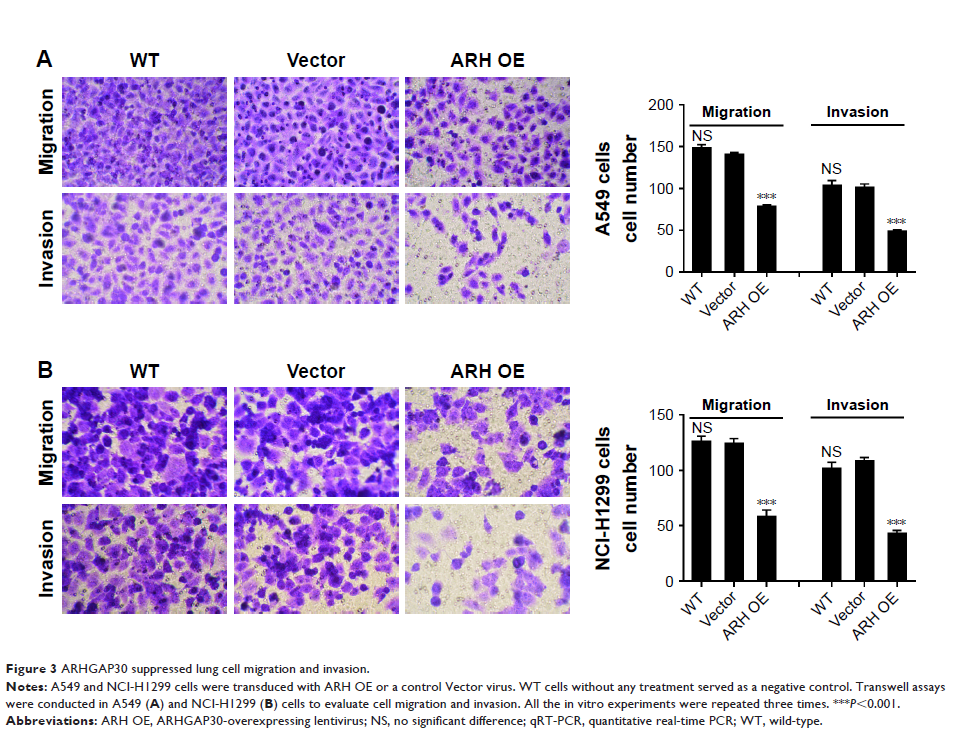
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and Transwell assays were conducted to detect cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion.
Results: ARHGAP30 expression was downregulated in specimens and cell lines
of lung cancer in comparison to non-cancerous specimens and normal bronchial
epithelial cell lines, respectively. Moreover, in vitro experiments
demonstrated that ARHGAP30 overexpression impeded the proliferative, migratory,
and invasive abilities of lung cancer cells. Moreover, bioinformatics analysis
with The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) lung cancer dataset showed a negative
association between ARHGAP30 expression and the Wnt signaling pathway. Enforced
expression of ARHGAP30 decreased the mRNA and protein levels of β-catenin,
c-Myc, matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9. Besides, the β-catenin
inhibitor XAV939 blocked the enhanced cell growth, migration, and invasion
caused by ARHGAP30 knockdown. Thus, the Wnt/β-catenin pathway mediated the
functions of ARHGAP30 in lung cancer cells.
Conclusion: ARHGAP30 acts as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer by suppressing
Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Keywords: ARHGAP30, Wnt/β-catenin, lung cancer, proliferation, metastasis