108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于树突状细胞的疫苗治疗对高级别胶质瘤患者的疗效和安全性分析:一个系统评价和荟萃分析
Authors Li C, Liu T, Zhou B, Zhou Y, Yu H, Sun Y
Received 20 June 2018
Accepted for publication 13 September 2018
Published 24 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 7277—7293
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S177768
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Background: Dendritic cell (DC)-based vaccine is a promising therapy for
high-grade gliomas (HGGs); however, its actual effectiveness still remains
controversial. This meta-analysis aims to extensively evaluate the efficacy and
safety of DC vaccine for HGG patients.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, the Cochrane Library, EMBASE,
Medline, and Web of Science for relevant parallel randomized controlled trials
(RCTs) and properly controlled non-randomized studies (NRS) published in
English. Two investigators reviewed all the texts and extracted information
regarding overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and adverse
events (AEs) from eligible studies. Sensitivity analyses and subgroup analyses
were also conducted.
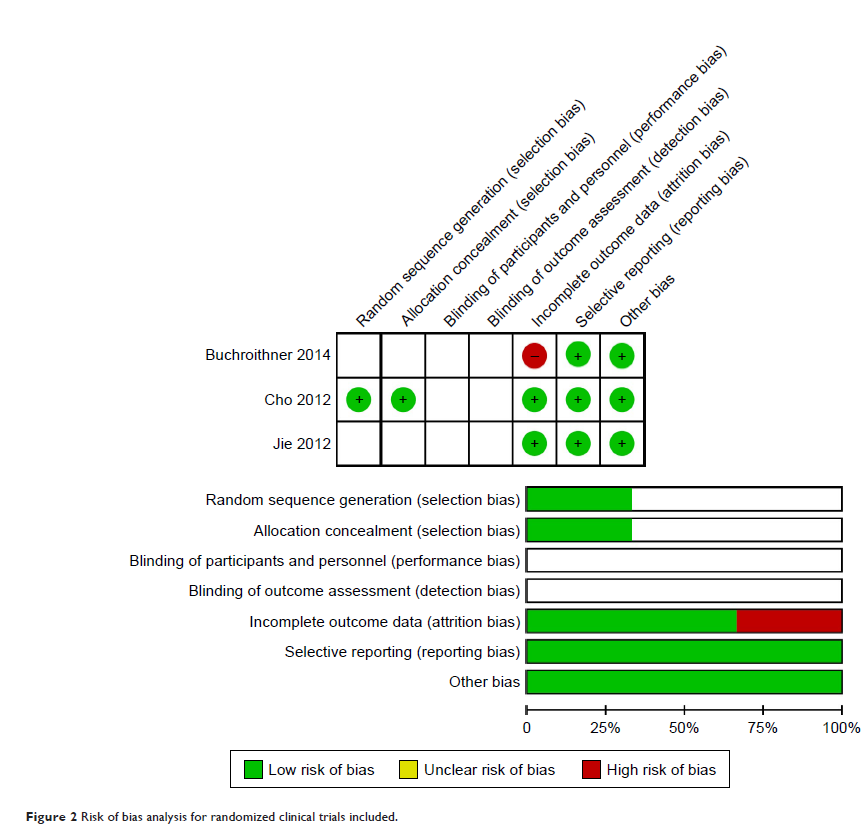
Results: Of 353 suitable studies, 13 studies (three RCTs and ten NRS)
involving 944 patients were finally included. Compared to the control therapy
group (CT group), the DC group showed better OS and PFS without serious AEs.
Subgroup analysis showed that trials designed as NRS obtained better results in
the DC group in this study; however, no specific subgroup regarding dosages,
cycles or injection routes was found to be superior in the DC group compared to
the CT group.
Conclusion: DC vaccine can significantly improve OS and PFS, with acceptable
toxicity, of HGG patients. Nevertheless, further studies are needed to verify
this conclusion.
Keywords: dendritic cell, vaccine, glioblastoma multiforme, high-grade
gliomas, overall survival, progression-free survival