108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CircRNA CDR1as/miR-7 信号促进骨肉瘤的肿瘤生长,具有潜在的治疗和诊断价值
Authors Xu B, Yang T, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Liu S, Shen M
Received 25 June 2018
Accepted for publication 11 August 2018
Published 23 October 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 4871—4880
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S178213
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: The circular RNA (circRNA) antisense to the cerebellar
degeneration-related protein 1 transcript (CDR1as)/micro RNA-7(miR-7) signal
axis has been investigated in many diseases via regulation of the target genes
of miR-7, which participates in the carcinogenesis and metastasis. However, the
clinical role and function of CDR1as/miR-7 pathway in osteosarcoma (OS) remain
to be identified.
Materials and
methods: Noncancerous bone tissues (n=18) and
OS tissues (n=38) were used to determine the expressions and roles of CDR1as
and miR-7. We knocked down the expression of CDR1as via siRNAs in OS cell lines
to analyze its function in vitro and in vivo.
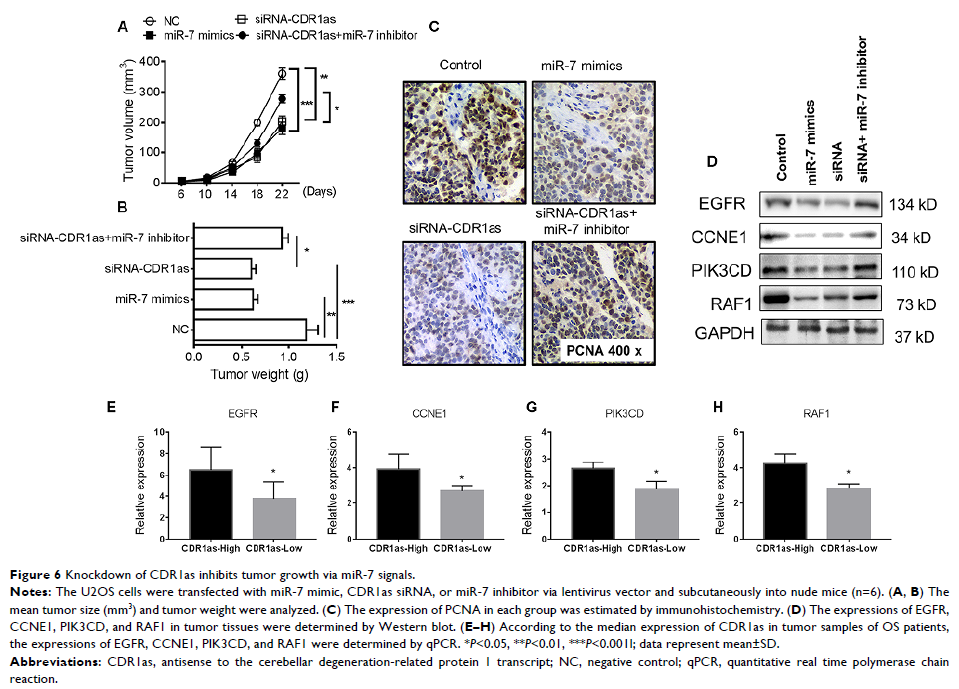
Results: CDR1as was upregulated in OS tissues with significant diagnostic value
(cutoff value: 1.613). OS patients with high tumor size, Enneking stage, and
distant metastasis have high CDR1as levels, but the miR-7 as tumor suppressor
negatively correlated with CDR1as. Inhibition of CDR1as in OS cell lines U2OS
and MG63 with high CDR1as levels, leading to de-repressed miR-7 levels,
impaired cell vitality and increased apoptosis and G1/S arrest in parallel with
reduced ability of cell migration, which, however, could be restored by miR-7
inhibitor. Mechanistically, knockdown of CDR1as could restore the availability
of miR-7 and inhibit the target genes of miR-7 including EGFR , CCNE1 , PI3KCD , and RAF1 . Moreover, CDR1as also
upregulated N-cadherin and inhibited E-cadherin to promote the
epithelial–mesenchymal transition via miR-7 for cell migration. CDR1as
inhibition in vivo also induced tumor regression with decreased PCNA levels,
and miR-7 inhibitor could reverse these effects via upregulation of EGFR , CCNE1 , PI3KCD , and RAF1 . The expressions of these
genes were confirmed to be higher in CDR1as-high OS samples than in CDR1as-low
OS samples.
Conclusion: These findings suggested that the CDR1as/miR-7 signal axis could be the
molecular target for the treatment of OS.
Keywords: CDR1as, miR-7, osteosarcoma, apoptosis, EMT