108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过使用含有环糊精的纳米悬浮液增强氟伐他汀的口服生物利用度
Authors Li J, Yang M, Xu WR
Received 15 June 2018
Accepted for publication 3 September 2018
Published 23 October 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 3491—3499
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S177316
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Background: In this study, fluvastatin (FVT) nanosuspensions containing cyclodextrin
were developed to improve oral bioavailability.
Methods: FVT nanosuspensions containing cyclodextrin were prepared by a
high pressure homogenization technique. The nanosuspensions system was then
characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), particle size,
differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and powder X-ray diffractometry (PXRD).
In addition, in vitro drug release properties, pharmacokinetics and
pharmacodynamics were also investigated in detail.
Results: After lyophilization, the nanosuspensions could be redispersed gently
and with a narrow particle size distribution, but the particle size has no
obvious change. The powder X-ray diffraction and differential scanning
calorimetry of FVT nanosuspensions showed that FVT existed in amorphous form in
nanosuspensions. In vitro release, FVT nanosuspensions have sustained-release
properties. Meanwhile, FVT nanosuspensions could significantly modify the
pharmacokinetic profile and increase the bioavailability of FVT by more than
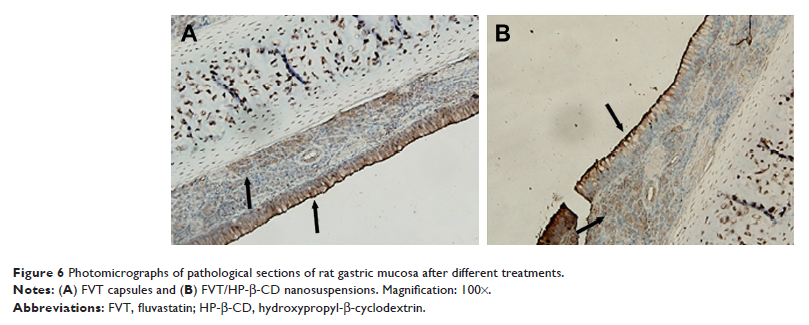
2.4-fold in comparison with the FVT capsules group. In vivo irritation test
showed that there was almost no evidence of hemorrhagic mucosal erosion and
intestinal villus destruction in rat gastric mucosa.
Conclusion: The combination of nanocrystallization and cyclodextrin
complexation techniques is a new attempt to formulate poorly water-soluble FVT.
Keywords: fluvastatin, HP-β-CD, nanosuspensions, bioavailability, irritation
test