108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

剖宫产术后 24 小时内使用舒芬太尼 - 曲马多的不同组合缓解疼痛的比较: 一项回顾性研究
Authors Cao X, Zhang XW
Received 17 June 2018
Accepted for publication 30 July 2018
Published 23 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2445—2451
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S177500
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael Schatman
Introduction: Postcesarean section pain management is important for both the
mother and the newborn. This study compared the analgesic effects and incidence
of adverse events associated with intravenous patient-controlled analgesia
(iv-PCA), using different sufentanil–tramadol combinations for postoperative
pain control.
Methods: Parturients (n=5,794) who had been scheduled for cesarean section
under neuraxial anesthesia and had received iv-PCA between September 2013 and
March 2017 were retrospectively analyzed. These patients were assigned to three
groups, based on different sufentanil–tramadol combinations: ST1 (n=1,347), ST2
(n=2,401), and ST3 (n=2,046). The analgesic efficacy, total drug consumption,
and incidence of adverse effects within 24 hours after surgery were compared
among the three groups.
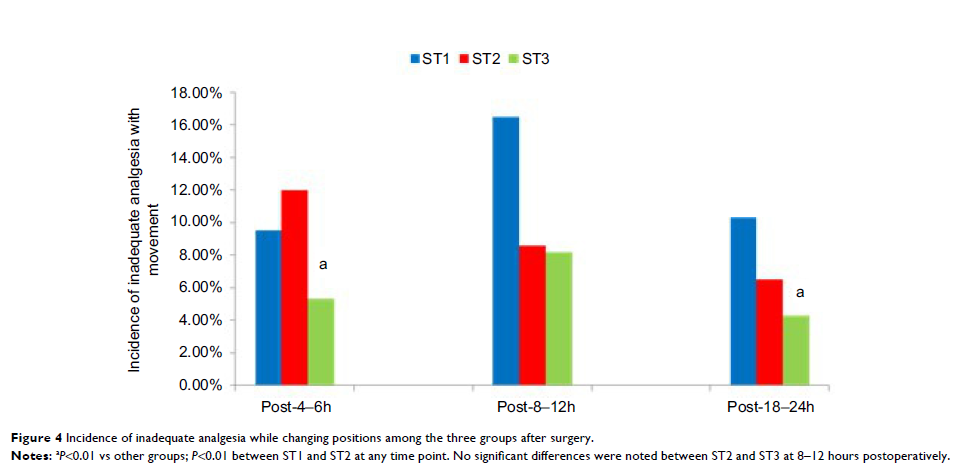
Results: The ST3 group had lower visual analog scale pain scores at rest
and with movement at all time points during the first 24 hours postoperatively
than the other two groups (P <0.01,
Bonferroni corrected). The sufentanil dosage administered to the ST3 group was
lower, and the tramadol dosage was higher than those administered to the other
groups within 24 hours after surgery (P <0.01,
Bonferroni corrected). Moreover, all parturients scored 2 points on the Ramsay
sedation scale. Adverse reactions such as pruritus and respiratory depression
were not observed in any group. No significant differences were noted in the
incidence of nausea/vomiting, abdominal distension, and dizziness among the
three groups (P >0.05).
Conclusion: The visual analog scale scores for postoperative pain decreased as
the concentrations of sufentanil and tramadol administered in iv-PCA moderately
increased over 24 hours after surgery. This analgesic strategy resulted in a
significant reduction in the total sufentanil requirement without increasing
the incidence of adverse effects.
Keywords: patient-controlled analgesia, sufentanil, tramadol, VAS score,
cesarean section