108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

低氧激活的前药和氧化还原反应纳米载体
Authors Zeng Y, Ma J, Zhan Y, Xu X, Zeng Q, Liang J, Chen X
Received 1 June 2018
Accepted for publication 22 August 2018
Published 18 October 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 6551—6574
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S173431
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
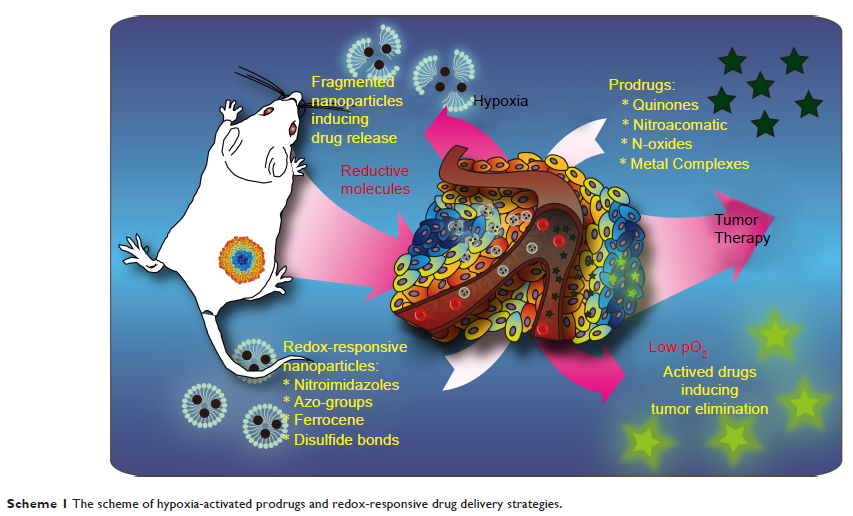
Abstract: Hypoxia is one of the marked features of malignant tumors, which is
associated with several adaptation changes in the microenvironment of tumor
cells. Therefore, targeting tumor hypoxia is a research hotspot for cancer
therapy. In this review, we summarize the developing chemotherapeutic drugs for
targeting hypoxia, including quinones, nitroaromatic/nitroimidazole, N-oxides,
and transition metal complexes. In addition, redox-responsive bonds, such as
nitroimidazole groups, azo-groups, and disulfide bonds, are frequently used in
drug delivery systems for targeting the redox environment of tumors. Both
hypoxia-activated prodrugs and redox-responsive drug delivery nanocarriers have
significant effects on targeting tumor hypoxia for cancer therapy.
Hypoxia-activated prodrugs are commonly used in clinical trials with favorable
prospects, while redox-responsive nanocarriers are currently at the
experimental stage.
Keywords: antitumor drugs, hypoxia, nanoparticles, redox-sensitive, tumor therapy