108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

预处理淋巴细胞/单核细胞比例对腹膜后脂肪肉瘤患者根治性切除术后的预后意义
Authors Luo P, Cai W, Yang L, Chen S, Wu Z, Chen Y, Zhang R, Shi Y, Yan W, Wang C
Received 19 April 2018
Accepted for publication 9 August 2018
Published 18 October 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 4727—4734
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S171602
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Luzhe Sun
Background: The aim of this study was to evaluate the prognostic value of
pretreatment inflammatory biomarkers in retroperitoneal liposarcoma (RPLS)
patients after radical resection.
Patients and
methods: One hundred patients with RPLS
who underwent radical resection between September 2004 and October 2010 at
Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center were included in this study. Laboratory
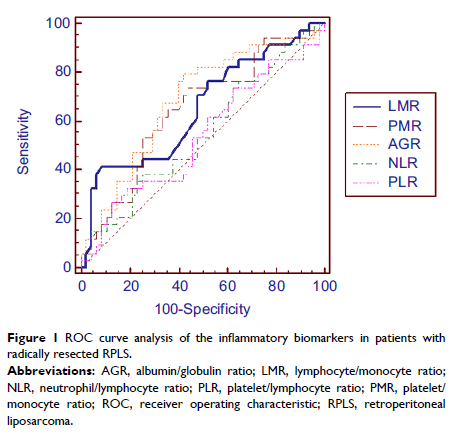
tests of peripheral blood were sampled before surgery. The optimal cutoff
values of systemic inflammatory markers were defined by receiver-operating
curve analyses. Curves of disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS)
were obtained by the Kaplan–Meier method. Cox proportional hazards regression
modeling was used to perform univariate and multivariate analyses.
Results: The median follow-up time was 53 months. The median DFS and OS were 27
and 86 months, respectively. On the basis of the optimal cutoff value of 3, 24
patients were classified into low lymphocyte/monocyte ratio (LMR) group and 76
patients into high LMR group. In univariate analysis, low LMR group had
significantly shorter DFS (P <0.001) and OS
(P <0.001) compared to high LMR
group. In multivariate analysis, low LMR was demonstrated as an independent
negative prognostic factor for both DFS (HR=2.854, 95% CI=1.392–5.851, P =0.004) and OS (HR=3.897, 95%
CI=1.681–9.033, P =0.002).
Conclusion: Pretreatment LMR is a useful prognostic marker in RPLS patients
after radical resection.
Keywords: retroperitoneal liposarcoma, inflammatory biomarkers, prognosis, lymphocyte,
monocyte ratio