108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA UCA1 敲除通过调节 miR-204/IGFBP5 轴抑制乳头状甲状腺癌的增殖和侵袭
Authors Liu H, Li R, Guan L, Jiang T
Received 27 May 2018
Accepted for publication 9 August 2018
Published 18 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 7197—7204
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S175467
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Background: Long noncoding RNA (LncRNA) UCA1 has been reported to function as
an oncogene in multiple cancers. However, the biological roles and underlying
mechanism of UCA1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) remain unclear. This
study aimed to investigate the underlying function of UCA1 on thyroid cancer
progression.
Materials and
methods: A series of experiments involving
Cell Counting Kit-8, wound-healing, and transwell invasion assays were
conducted to determine the cellular capabilities of proliferation, migration,
and invasion, respectively. Binding sites between UCA1 and miR-204 were
identified using a luciferase reporter system, whereas mRNA and protein
expression of target genes were determined by real-time quantitative reverse
transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blot, respectively.
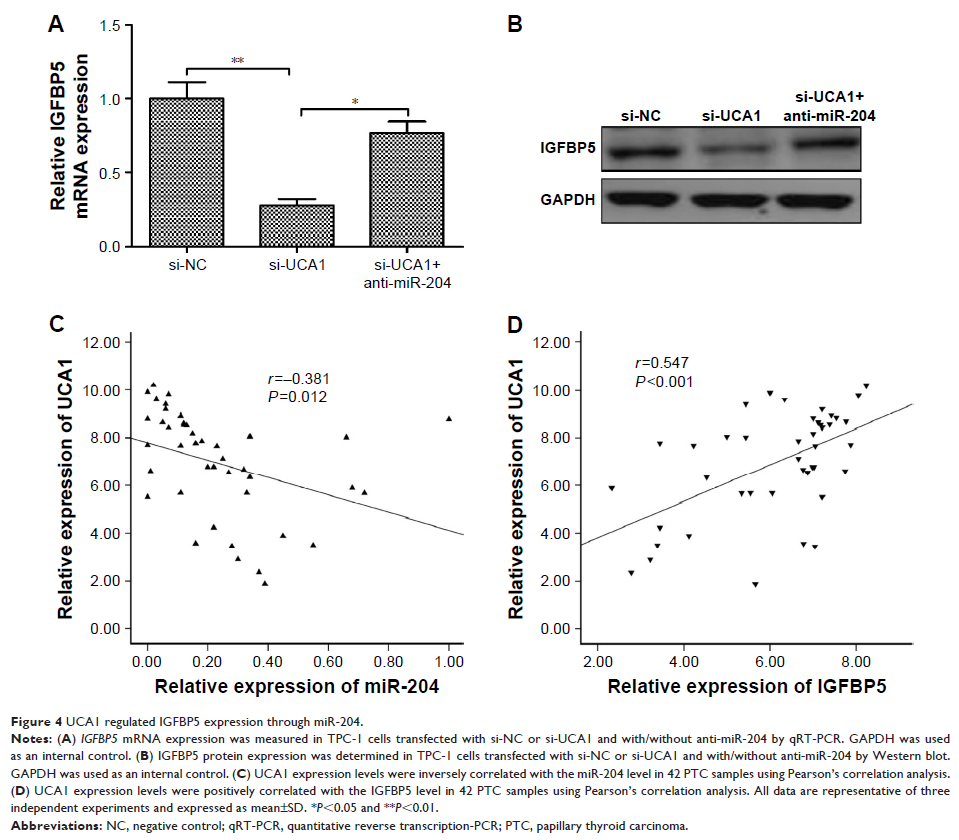
Results: The results revealed that UCA1 was upregulated in PTC tissue and cell
lines. UCA1 knockdown significantly suppressed the cell proliferation,
migration, and invasion of TPC-1 cells. Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase
reporter assay verified the complementary binding within UCA1 and miR-204 at
the 3'-UTR. Moreover, miR-204 inhibition reversed the UCA1 knockdown-mediated
inhibitory effect on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. We also found
that UCA1 could regulate expression of IGFBP5, a direct target of miR-204 in
PTC.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that UCA1 exerts activity of oncogenes in PTC
through regulating miR-204/IGFBP5 axis.
Keywords: papillary thyroid carcinoma, lncRNA, UCA1, miR-204, IGFBP5