108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

术前白蛋白与球蛋白的比值是泌尿系统癌症的重要预后指标:一项综合分析
Authors Zhang Y, Wang L, Lin S, Wang R
Received 26 June 2018
Accepted for publication 7 September 2018
Published 17 October 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 4695—4708
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S178271
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Raphael Catane
Background: Emerging studies reported that preoperative albumin-to-globulin
ratio (AGR) correlated with tumor progression and prognosis in several types of
cancer. The aim of this study was to systematically explore the association
between preoperative AGR and clinical outcomes in cancers of the urinary
system.
Methods: Relevant articles were searched in PubMed, Embase and Web of
Science by two independent investigators from inception to June 1, 2018.
Eligible studies were selected based on predetermined selection criteria.
Summarized HRs or ORs and 95% CIs were calculated for prognosis and
clinicopathologic features with the fixed-effects or random-effects models.
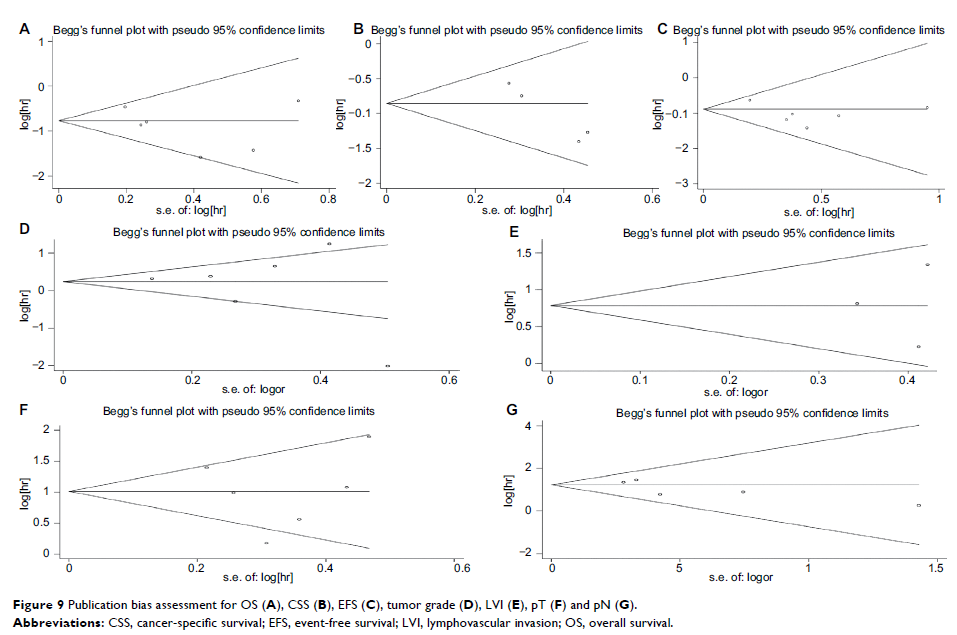
Results: Eight cohort studies comprising 2,668 patients were included for
analysis. The pooled results showed that a low AGR significantly correlated
with poor OS (HR: 0.38, 95% CI: 0.27–0.48, P <0.001),
worse cancer-specific survival (CSS) (HR: 0.36, 95% CI: 0.22–0.50, P <0.001) and inferior
event-free survival (EFS) (HR: 0.36, 95% CI: 0.25–0.48, P <0.001) in urologic cancers.
In addition, patients in low and high AGR groups showed significant differences
in lymphovascular invasion (P <0.001), pT
status (P <0.001) and pN status (P <0.001).
Conclusion: Preoperative AGR might be a valuable, cheap and reproducible
prognostic biomarker in urologic cancers following surgical resection.
Keywords: albumin-to-globulin ratio, urologic cancer, prognosis, clinical
features