108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Nesfatin-1 和皮质醇:中度和重度抑郁症的潜在新型诊断生物标志物
Authors Xu YY, Ge JF, Liang J, Cao Y, Shan F, Liu Y, Yan CY, Xia QR
Received 8 August 2018
Accepted for publication 14 September 2018
Published 16 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 495—502
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S183126
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Igor Elman
Background: This study aimed to determine whether plasma nesfatin-1, cortisol,
and inflammatory cytokines could be used as novel noninvasive biomarkers for
the diagnosis of moderate and severe depressive disorder (MSDD).
Materials and
methods: A total of 70 patients with MSDD and
70 healthy subjects were assessed. Patients with MSDD were selected from Hefei
Fourth People’s Hospital, Anhui Mental Health Center, and subjects in the
control group were selected from healthy volunteers. Hamilton Depression Rating
Scale-17 (HAMD-17) was used to evaluate the two groups. ELISA was used for the
measurement of plasma nesfatin-1, cortisol, IL-6, C-reactive protein (CRP), and
tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) levels. The diagnostic value of plasma
nesfatin-1, cortisol, IL-6, CRP, and TNF-α for MSDD was assessed.
Results: Compared to healthy controls, the HAMD-17 scores and average
nesfatin-1, cortisol, IL-6, and CRP levels in patients with MSDD were
significantly increased. Moreover, multivariate linear regression analysis
showed that HAMD-17 score was positively associated with plasma nesfatin-1 and
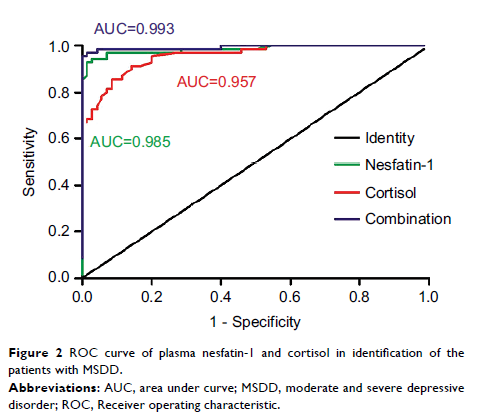
cortisol. Furthermore, the results of the receiver operating characteristic
(ROC) curve analysis revealed an area under curve (AUC) of 0.985 with 94.3%
sensitivity and 97.1% specificity of nesfatin-1, and an AUC of 0.957 with 91.4%
sensitivity and 85.7% specificity of cortisol in discriminating patients with
MSDD from healthy volunteers. A combined ROC analysis using nesfatin-1 and
cortisol revealed an AUC of 0.993 with a sensitivity of 97.1% and a specificity
of 98.6% in separating patients with MSDD from healthy volunteers.
Conclusion: These results suggest that plasma nesfatin-1 and cortisol might be
potential novel biomarkers for the diagnosis of MSDD.
Keywords: C-reactive protein, cortisol, IL-6, depression, nesfatin-1, tumor
necrosis factor-α