108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CAV3.1 敲除通过抑制 AKT 来遏制前列腺癌细胞的细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Hu SB, Li L, Huang W, Liu J, Lan G, Yu S, Peng L, Xie X, Yang L, Nian Y, Wang Y
Received 3 May 2018
Accepted for publication 13 June 2018
Published 15 October 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 4603—4614
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S172948
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Aberrant expression of CAV3.1, one of T-type Ca2+ channels, is reported to exert important functions in pathological
processes, including carcinogenesis. However, its expression pattern and
function in prostate cancer (PCa) remains unclear.
Materials and
methods: The expression pattern of CAV3.1 was
analyzed in multiple ways, including online analysis in Oncomine database,
experimental analyses in cell lines, and collected clinical specimens using
immunohistochemistry, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain
reaction, and Western blot. Then, CAV3.1 was downregulated in PCa cells to
explore its functions.
Results: Upregulated CAV3.1 in PCa tissues and cells was confirmed by
analyzing mRNA expression datasets from Oncomine and quantitative reverse
transcription polymerase chain reaction detection, respectively. Accordingly,
significantly higher CAV3.1 protein level in PCa tissues specimens than that in
benign prostatic hyperplasia tissues was indicated by immunohistochemical
staining. In addition, CAV3.1 upregulation was positively associated with
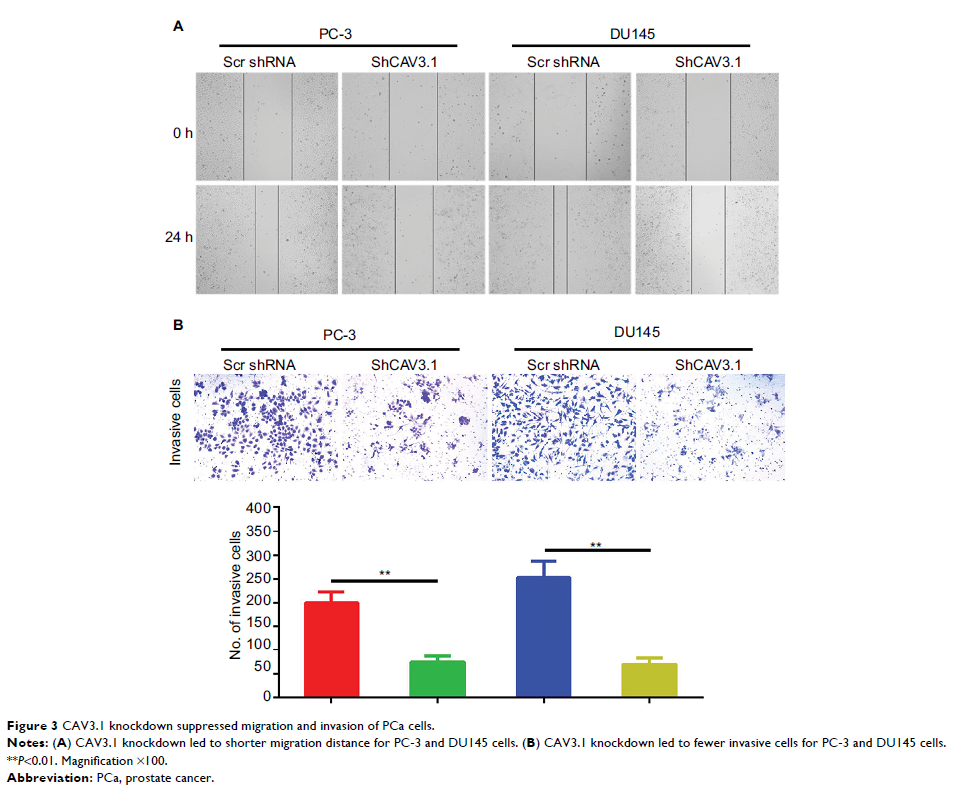
metastasis. Depletion of CAV3.1 impaired the proliferation, migration, and
invasion ability of PCa cells demonstrating by cell functional experiments,
such as CCK-8, cell cycle distribution, plate clone formation, scratch wound
healing, and transwell invasion assays. Mechanistically, due to constrained Akt
activity, CAV3.1 knockdown resulted in decreased level of CCND1, N-cadherin,
and Vimentin, and increased level of E-cadherin whose expressions could be
reversed by ectopic Akt expression. Similarly, ectopic Akt expression also
rescued the inhibitory effects of CAV3.1 knockdown on cell functions like
proliferation and migration in PCa cells.
Conclusion: Upregulated CAV3.1 is positively associated with the development
of PCa. CAV3.1 knockdown can inhibit PCa cell proliferation, migration, and
invasion by suppressing AKT activity.
Keywords: CAV3.1, PCa, AKT signaling, proliferation, invasion