108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

升高的血清 IL-6 和脂联素水平与中国老年人的虚弱和身体功能有关
Authors Ma L, Sha G, Zhang Y, Li Y
Received 20 July 2018
Accepted for publication 15 September 2018
Published 15 October 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 2013—2020
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S180934
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Wu
Purpose: Frailty is associated with adverse health outcomes. Its biological
markers are essential to enhance diagnostic ease and
would contribute to surveillance of the condition. Considering the involvement
of pro-inflammatory and nutritional states in frailty, we aimed to investigate
whether inflammatory mediators and adipokines are associated with frailty and
their relationship with physical function.
Patients and
methods: We recruited 130 older adults (90
nonfrail participants and 40 frail participants, mean age: 72.80±8.61 years)
who underwent a comprehensive medical history and frailty assessment. The
biochemical indicators (eg, blood urea nitrogen [BUN], high-density lipoprotein
[HDL], and hemoglobin [HGB]), insulin pathway (glucose, insulin, and
insulin-like growth factor 1 [IGF-1]), circulating inflammatory biomarkers
(IL-6, tumor necrosis factor receptor 1, and C-reactive protein), and
adipokines (adiponectin, vaspin, and leptin) were compared between the two
groups. We further analyzed their correlation with physical function.
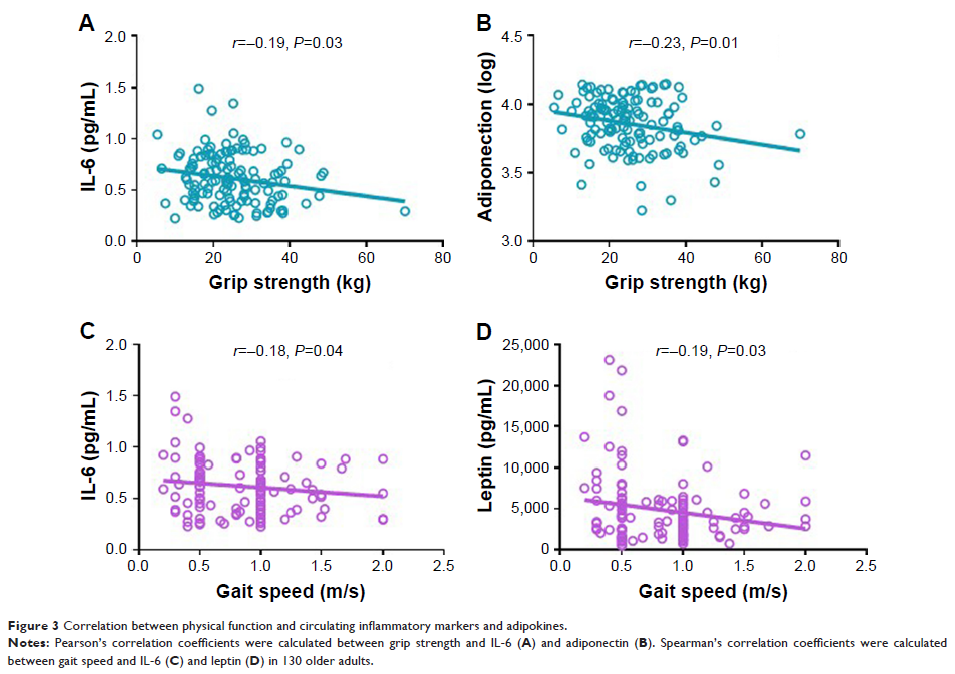
Results: Frail older adults showed higher levels of BUN, IL-6, adiponectin,
vaspin, and glucose and lower levels of IGF-1, HDL, and HGB compared with
nonfrail participants. Serum IL-6 levels were negatively correlated with both
grip strength (P =0.03) and gait speed (P =0.04). Levels of circulating
adiponectin and leptin were adversely correlated with grip strength (P =0.01) and gait speed (P =0.03), respectively. After
adjustment for age and sex, the only markers correlated with physical function
were IL-6 (r =-0.180, P =0.044) and adiponectin (r =-0.195, P =0.029).
Conclusion: High levels of IL-6, adiponectin, vaspin, and glucose as well as
low levels of IGF-1 were found in frail older adults. Furthermore, IL-6,
adiponectin, and leptin levels were negatively correlated with physical
function, suggesting that inflammatory mediators and adipokines are biomarkers
for frailty and decreased function in older adults.
Keywords: adipokine, adiponectin, biomarker, frailty, inflammation, IL-6