108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国南方败血症患者血液标本中常见可动遗传因子检测和多重耐药革兰阴性杆菌的基因分型
Authors Rui Y, Lu W, Li S, Cheng C, Sun J, Yang Q
Received 14 February 2018
Accepted for publication 2 June 2018
Published 12 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1741—1750
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S165513
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eric Nulens
Background: Integron, ISCR1 and complex class 1 integrons lead bacteria to
become resistant to antibiotic regimens. The aim of this study was to detect
common mobile genetic elements of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacilli and
evaluate the genotyping of these bacilli in blood specimens from septicemia
patients in southern China.
Methods: A total of 837 Gram-negative bacilli including 578 strains
containing Enterobacteriaceae and 259 strains
containing non-fermentative bacilli were investigated in blood samples
collected from septicemia patients between 2011 and 2014 in southern China.
Mobile genetic elements, such as class 1 integrons, the insertion sequence
common region 1 (ISCR1), and complex class 1 integrons, were detected from the
837 strains.
Results: Twenty-seven types of gene cassette arrays were found among 837
strains in which 492 (58.8%) class 1 integron-positive isolates and 254 (51.6%)
gene cassette-positive isolates were found, including the first description of
two types, aac A4-bla IMP-1-bla OXA-30-cat B3 and aac (6′)-II-aad A13-cml A8-bla OXA-10, in the corresponding species and two gene cassettes, putative helicase
and aad A-like, originally detected in
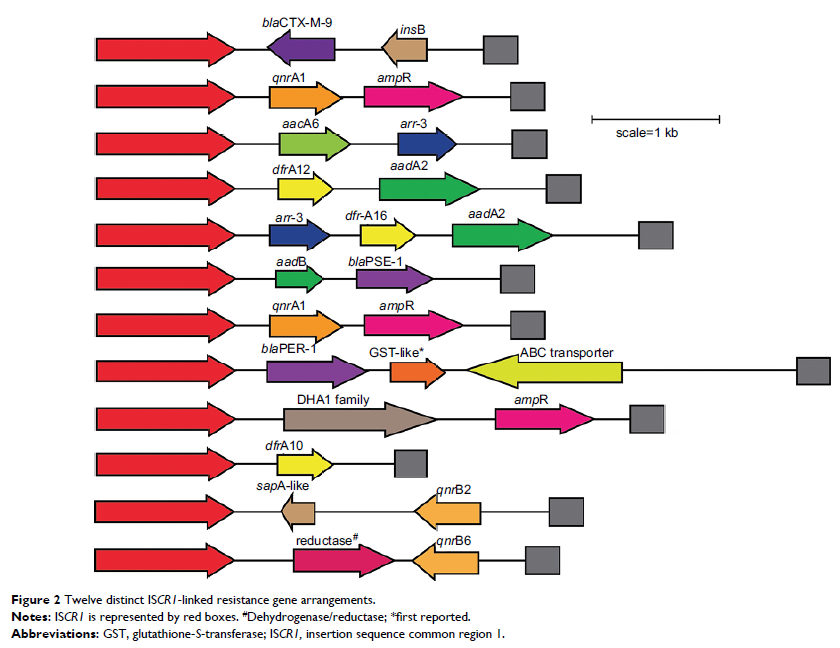
integrons. Twelve types of ISCR1-linked resistance gene regions in 196
ISCR1-positive bacilli and seven different types of complex class 1
integron-positive strains were obtained including four distinct complex class 1
integrons that have never been described in any species. Enterobacterial
repetitive intergenic consensus (ERIC)-PCR fngerprinting showed that isolates
with identical gene profles were clonally unrelated.
Conclusion: Our results indicated that we should pay more attention to enhance
the quality of infection control measures and prevent hospital infection, so as
to avoid the outbreak of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacilli.
Keywords: septicemia, multidrug-resistant, integron, ISCR1 , complex class 1 integrons