108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-638 的下调促进乳腺癌的发展并且与乳腺癌患者的预后相关
Authors Li M, Wang J, Liu H
Received 31 July 2018
Accepted for publication 4 September 2018
Published 12 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6871—6877
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S182034
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: Breast cancer is the most common tumor among women. miR-638 has
been demonstrated to play an important role in various cancers.
Purpose: In this study, we aimed to investigate the function and prognostic
value of miR-638 in breast cancer.
Methods: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis was used
to evaluate the expression of miR-638 in breast cancer tissues and cell lines.
The correlation of miR-638 with clinicopathological features was analyzed using
the chi-squared test. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis and Cox regression assay
were performed to investigate the prognostic value of miR-638 in breast cancer
patients. The effects of miR-638 on the biological behavior of breast cancer
cells were evaluated using functional assays.
Results: The expression of miR-638 was downregulated in breast cancer
tissues and cell lines (all P <0.05).
Decreased expression of miR-638 was significantly correlated with lymph node
metastasis (P =0.015) and TNM stage (P =0.021). Patients with low
miR-638 expression had shorter overall survival compared with those with high
levels (Log-rank P =0.025). The
miR-638 could be considered as an independent prognostic factor for the
patients (HR =0.321, 95% CI =0.117–0.882, P =0.027).
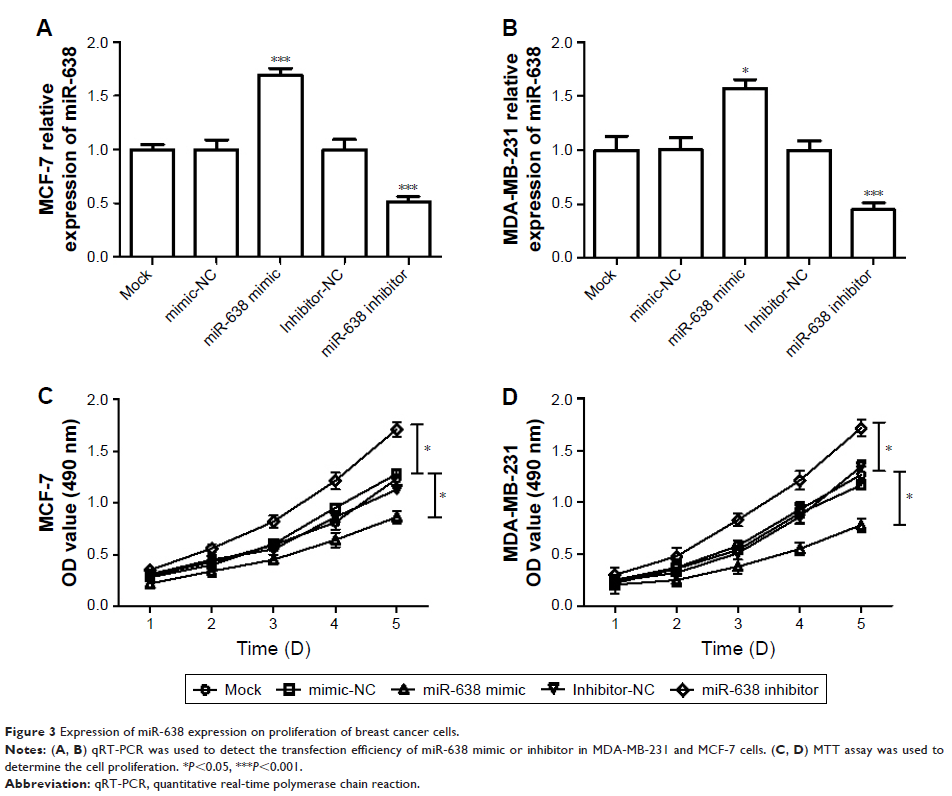
Downregulation of miR-638 was capable of promoting cell proliferation,
migration, and invasion in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells.
Conclusion: All the results indicate that miR-638 is a tumor suppressor in
breast cancer and is involved in the progression of breast cancer. Thus, it may
serve as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer.
Keywords: miR-638, cell proliferation, migration, invasion, prognosis,
breast cancer