108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:非编码 RNA NEAT1/miR-214-3p 最初通过 Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路对尿路上皮膀胱癌的阿霉素耐药性产生影响
Authors Guo Y, Zhang H, Xie D, Hu X, Song R, Zhu L
Received 14 April 2018
Accepted for publication 16 July 2018
Published 11 October 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 4371—4380
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S171126
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
***本文章已被撤回***
Background: Urothelial bladder cancer (UBC) is one of the most lethal
urological malignancies in the world. Patients with UBC are routinely given
chemotherapy which results in a median survival of 12-15 months.
Nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) functions as an oncogene and
could be used as a therapeutic target for human UBC. However, the involvement
of NEAT1 in doxorubicin (DOX) resistance of UBC has been poorly demonstrated.
Methods: Quantitative Real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to detect the
expression levels of NEAT1 and miR-214-3p in UBC tissues and cells.
Bioinformatics prediction, RNA pull-down and qRT-PCR were used to assay the
regulation manner of NEAT1 and miR-214-3p. Loss/gain function of NEAT1 and
miR-214-3p together with western blot, drug resistance assay and flow cytometry
were used to explore the influence of NEAT1 in DOX resistance was correlative
with miR-214-3p. Finally, luciferase assay system was applied to determine the
Wnt/β-catenin signal activity.
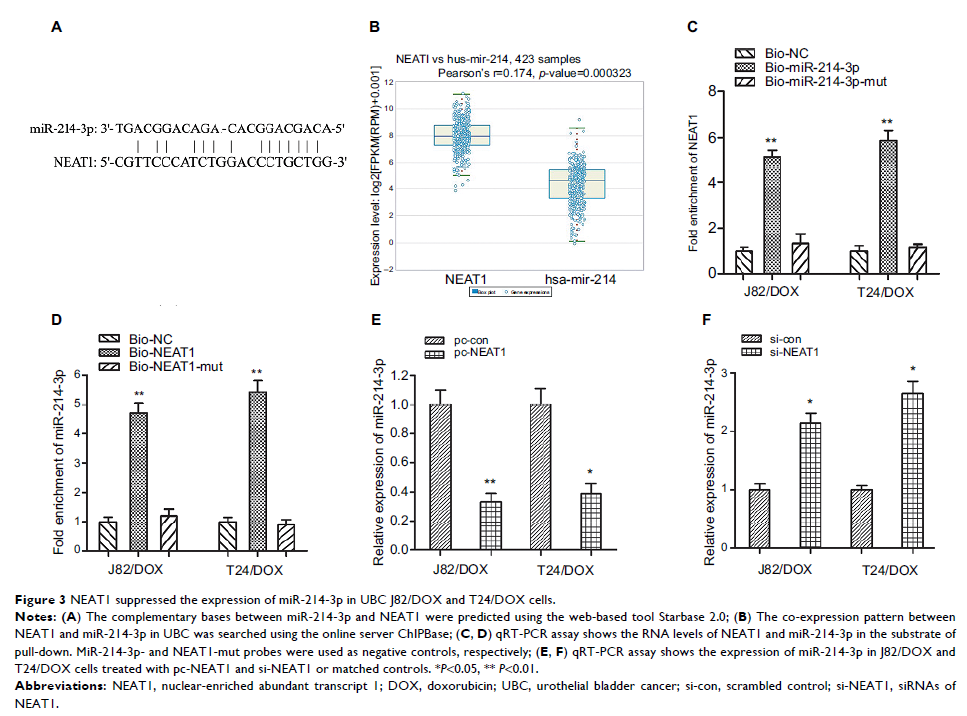
Results: NEAT1 was upregulated and miR-214-3p was downregulated in
DOX-resistant UBC tissues and cells. NEAT1 knockdown inhibited J82 and T24
cells to DOX chemosensitivity by negatively regulating miR-214-3p expression.
NEAT1/miR-214-3p contributed to DOX resistance of UBC preliminary through the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Conclusion: NEAT1 contributed to DOX resistance of UBC through the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway partly by negatively regulating miR-214-3p expression.
Our findings will provide a promising ncRNA targeted therapeutic strategy for
UBC with DOX resistance.
Keywords: nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1, miR-214-3p, urothelial
bladder cancer, doxorubicin resistance, Wnt/β-catenin pathway