108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

AKIP1 上调促进结肠直肠癌的转移和进展,并预测患者的预后不良
Authors Jiang W, Yang W, Yuan L, Liu F
Received 18 September 2017
Accepted for publication 9 July 2018
Published 11 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6795—6801
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S151952
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background: A kinase-interacting protein 1 (AKIP1) has been reported to play
an important role in the development and progression of cancer. However, the
clinicopathological and biological roles of AKIP1 in colorectal cancer (CRC)
remain largely unknown. The aim of this study was to investigate AKIP1 protein
expression in CRC and determine the correlation between AKIP1 protein
expression and clinicopathological features, as well as prognosis in CRC
patients.
Materials and
methods: AKIP1 protein expression was
determined by immunohistochemical analysis using tissue microarrays of CRC. We
also used an siRNA approach to knock down AKIP1 expression and determine the
effect of AKIP1 on CRC cell migration by transwell analysis.
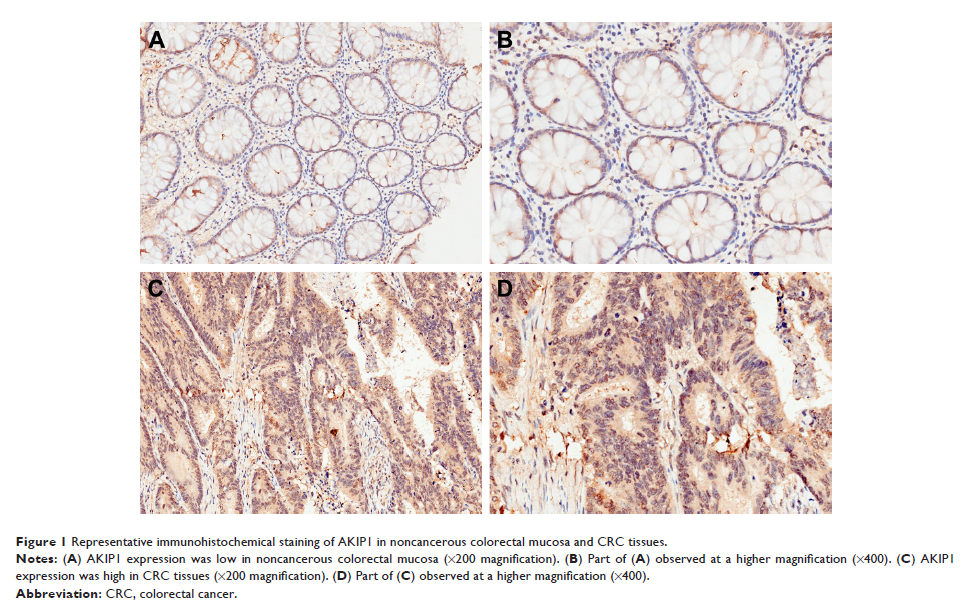
Results: AKIP1 expression in CRC tissue was significantly higher compared
with that of noncancerous colorectal mucosa (P <0.001).
Further analysis showed that AKIP1 expression was significantly associated with
tumor diameter, TNM stage, and lymph node metastasis (P <0.05). Kaplan–Meier survival
analysis demonstrated that patients with a positive AKIP1 expression had
significantly poorer overall survival rates when compared with those with
negative AKIP1 expression (P =0.031).
Multivariate analysis using the Cox proportional hazard model, however,
revealed that AKIP1 expression was not a significant independent prognostic
factor for CRC. Transwell assay showed that the migration potential of
si-AKIP1-transfected cells was significantly reduced when compared with control
cells.
Conclusion: Elevated AKIP1 expression may contribute to metastasis and progression
of CRC. Moreover, high AKIP1 expression in CRC significantly correlated with a
patient’s shorter survival time. Therefore, AKIP1 may be a useful prognostic
marker for CRC and a promising novel target for the treatment of CRC.
Keywords: AKIP1, colorectal cancer, metastasis, prognosis