108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-708-5p 通过抑制 Wnt3a/β-catenin 通路促进成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞的细胞凋亡并改善类风湿性关节炎
Authors Wu J, Fan W, Ma L, Geng X
Received 13 June 2018
Accepted for publication 20 July 2018
Published 10 October 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 3439—3447
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S177128
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Aim: MicroRNAs (miRNA) are a class of small, highly conserved noncoding RNA molecules, which contain 18–28 nucleotides and are involved in the regulation of gene expression. It has been proved that microRNAs play a very important role in several key cellular processes, such as cell differentiation, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis, as well as in autoimmune disease. One recently identified miRNA, miR-708-5p, has been demonstrated to have profound roles in suppressing oncogenesis in different types of tumors. However, the role of miR-708-5p in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) remains to be fully elucidated. Therefore, in this study, we are aiming to identify the role of miR-708-5p in RA.
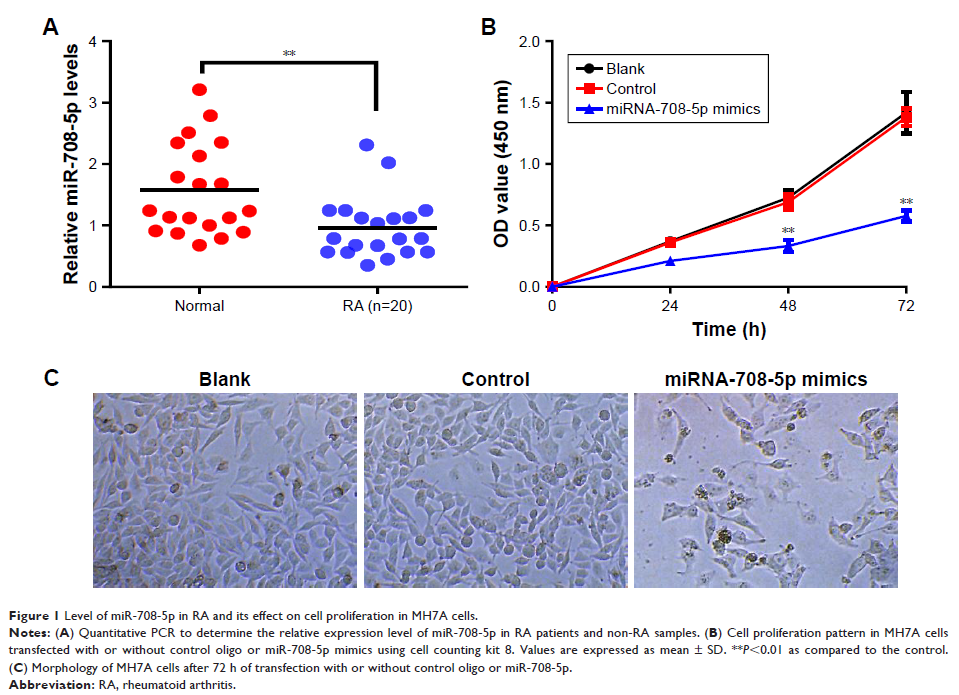
Methods: The expression level of miR-708-5p in synovial tissues of patients with RA is much lower than in non-RA controls. The effects of miR-708-5p on cell apoptosis, colony formation, and migration in fibroblast-like synoviocytes were assessed in MH7A cells.
Results: Results showed that delivery of miR-708-5p mimics into synovial fibroblasts MH7A could induce cell apoptosis and inhibit colony formation and migration. In addition, miR-708-5p mimics significantly inhibit Wnt3a/β-catenin pathway activity both in transcription and protein level, which could be reversed by the addition of R-spondin 1, an activator of Wnt pathway. R-spondin 1 could also reverse the inhibition of cell survival and proliferation, which was induced by miR-708-5p mimics in MH7A. Moreover, injection of miR-708-5p mimics into collagen-induced rat RA model could ameliorate the RA index and decrease Wnt3a/β-catenin expression in rat joint tissues.
Conclusion: Therefore, we concluded that miR-708-5p is likely to be involved in RA pathogenesis via inhibition of Wnt3a/β-catenin pathway.
Keywords: miR-708-5p, rheumatoid arthritis, cell proliferation, Wnt