108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

认知行为治疗抑郁症对改善中国乳腺癌患者失眠和生活质量的影响: 随机、对照、多中心试验的结果
Authors Qiu H, Ren W, Yang Y, Zhu X, Mao G, Mao S, Lin Y, Shen S, Li C, Shi H, Jiang S, He J, Zhao K, Fu Y, Hu X, Gu Y, Wang K, Guo X, He J
Received 16 April 2018
Accepted for publication 24 July 2018
Published 10 October 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 2665—2673
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S171297
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Purpose: Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for depression had been found to be effective in reducing depressive and anxiety symptoms in breast cancer survivors. It is not known whether CBT for depression would also improve insomnia and quality of life (QOL). The aim of this study was to investigate whether CBT for depression would improve insomnia and QOL in a randomized controlled multicenter trial.
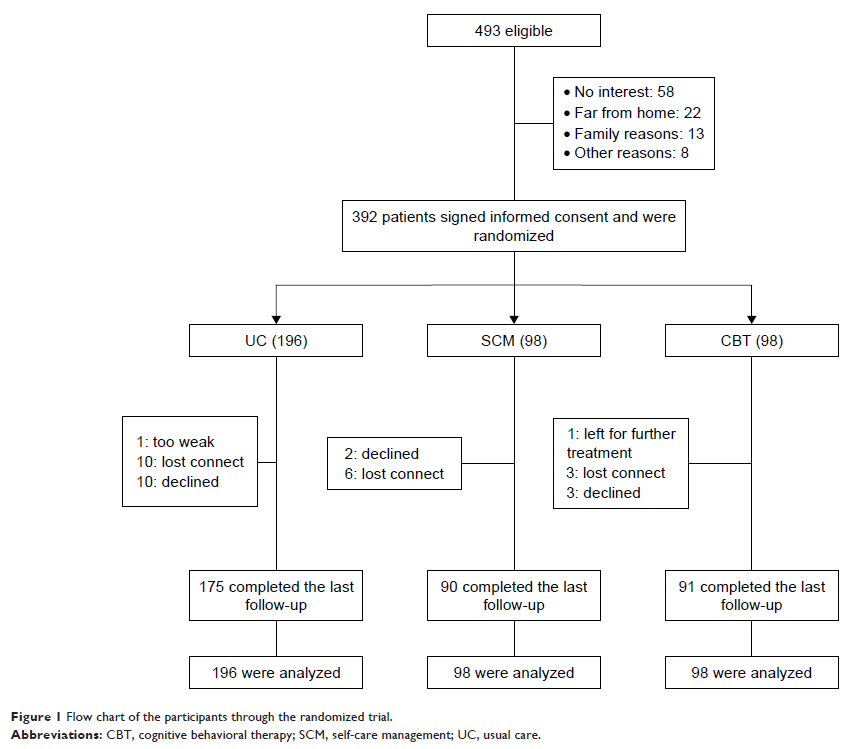
Patients and methods: In this study, breast cancer survivors (n=392) were randomly allocated to the following three groups: CBT (n=98), self-care management (SCM, n=98), and usual care (UC, n=196) in a ratio of 1:1:2. CBT and SCM received a series of nine sessions for 12 weeks, whereas UC received UC only. Insomnia and QOL were evaluated using Athens Insomnia Scale (AIS) and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast (FACT-B) questionnaire at baseline, 4, 12, and 24 weeks.
Results: There was a significant intergroup difference in AIS and FACT-B scores (both P <0.01). CBT showed less insomnia problems and better overall QOL compared with those in SCM and UC (both P <0.01). No significant differences were found between SCM and UC in insomnia problems and overall QOL. Moreover, the effects of CBT on insomnia and QOL were maintained during the follow-up period.
Conclusion: CBT for depression can be effective in improving insomnia problems and QOL in the Chinese breast cancer survivors.
Keywords: cancer, psychotherapy, sleep, prognosis