108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

质子泵抑制剂通过 TSC1/2 复合体和 Rheb 在体外和体内下调人胃腺癌细胞内的 V-ATPases/PI3K/Akt/mTOR/HIF-1α 信号通路,起到逆转多药耐药性的作用
Authors Chen M, Lu J, Wei W, Lv Y, Zhang X, Yao Y, Wang L, Ling T, Zou X
Received 31 December 2017
Accepted for publication 13 April 2018
Published 10 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6705—6722
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S161198
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Our study aimed to explore the effects of PPIs on reversing multidrug resistance (MDR) to chemotherapy in gastric cancer by inhibiting the expression of V-ATPases and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/ HIF-1α signal pathway.
Methods: The gastric cancer cell lines SGC7901 and the multidrug resistance cell lines SGC7901/MDR were pretreated by the pantoprazole or the esomeprazole, respectively. Real-time PCR was used to determine mRNA levels, and western blotting and immunofluorescent staining analyses were employed to determine the protein expressions and intracellular distributions of the V-ATPases, PI3K, Akt, mTOR, HIF-1α, P-gp and MRP1 before and after PPIs pretreatment. SGC7901/MDR cells were planted on the athymic nude mice. Then the effects of PPZ pretreatment and/or ADR were compared by determining the tumor size, tumor weight and nude mice weight.
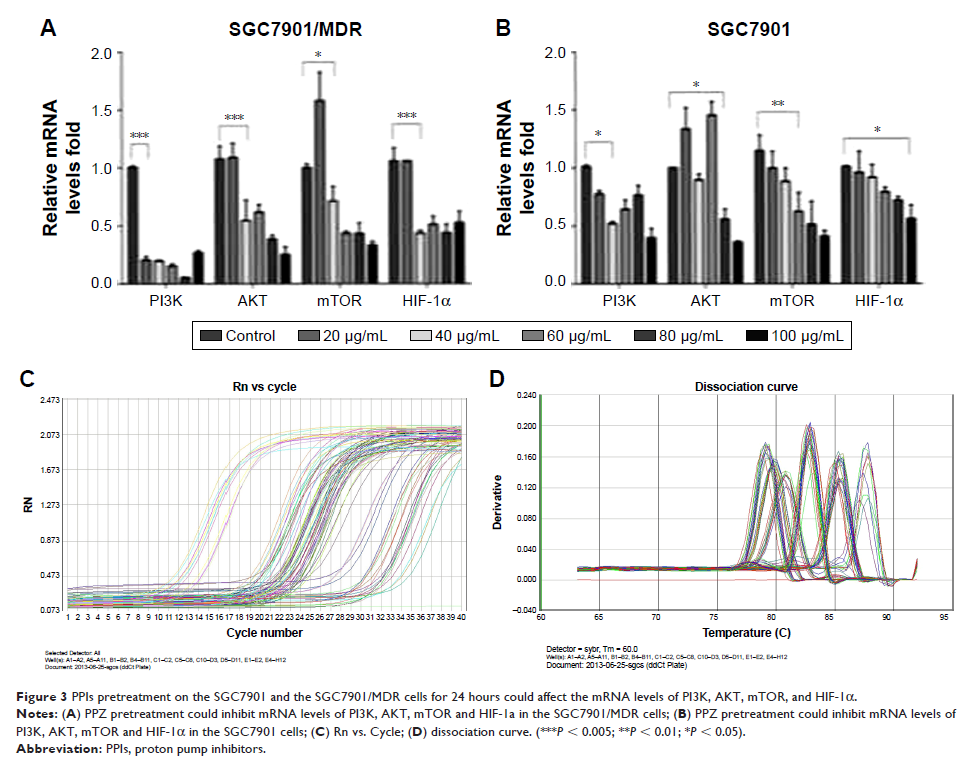
Results: PPIs pretreatment could inhibit mRNA levels of V-ATPases, MDR1 and MRP1, PI3K, Akt, mTOR and HIF-1α. PPIs inhibited V-ATPases and down-regulated the expressions of P- gp and MRP1. And further to block the expression of mTOR by Rapamycin could obviously inhibit the expressions of HIF-1α, P-gp and MRP1 in a dose-dependent manner. Therefore, PPIs inhibited the expressions of V-ATPases and then reversed MDR of the chemotherapy in gastric cancer by inhibiting P-gp and MRP1, and it could be speculated that the mechanism might be closely related to down-regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/HIF-1α signaling pathway. Meanwhile, PPIs also could inhibit the expressions of TSC1/TSC2 complex and Rheb which might be involved into regulating the signaling pathway intermediately. The weight growth rate of the mice bearing tumor in the treatment group was lower than that of the nude mice in the normal group, while the weight growth rate of the mice in control group was significantly lower than that of the normal group and the treatment group, presenting a downward trend.
Conclusion: Therefore, PPIs inhibited the expressions of V-ATPases and then reversed MDR of the chemotherapy in gastric cancer by inhibiting P-gp and MRP1, and it could be speculated that the mechanism might be closely related to down-regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/HIF-1α signaling pathway, and also to inhibiting the expressions of TSC1/TSC2 complex and Rheb which might be involved into regulating the signaling pathway intermediately.
Keywords: gastric adenocarcinoma, V-ATPases, tumor acidity, hypoxia, proton pump inhibitors, multidrug resistance, signaling pathway