108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Circ-DLG 1 促进食管鳞状细胞癌的增殖
Authors Rong J, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Zhu D, Sun H, Tang W, Wang R, Shi W, Cao XF
Received 30 May 2018
Accepted for publication 15 August 2018
Published 9 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6723—6730
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S175826
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a class of noncoding RNAs with closed loop structures. There has been growing evidence showing that circRNAs are involved in the pathogenesis of human diseases including various carcinomas. Our study is aimed to investigate the association between a new circRNA named circ-DLG1 (hsa_circ_0007203) and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) carcinogenesis.
Methods: The circ-DLG1 expression levels were detected by real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in cells, tissues, and plasmas. The correlation between circ-DLG1 expression and clinicopathologic features was then analyzed. The effect of circ-DLG1 expression on cell proliferation was evaluated in vitro by CCK8 assay and clone formation experiment. Finally, a network of circ-DLG1 with its targeted miRNA interactions and corresponding mRNAs was constructed.
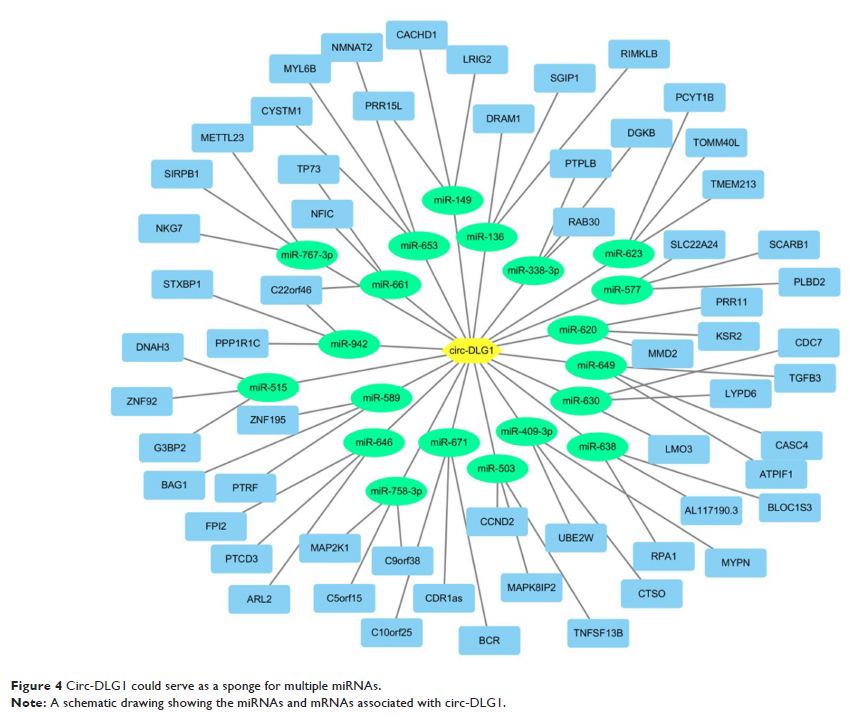
Results: circ-DLG1was found to be significantly upregulated in ESCC cells, tissues, and plasmas compared to normal cases. Furthermore, in vitro assays, TE10 and KYSE180, of the ESCC cell lines demonstrated that knockdown of circ-DLG1 reduced cell proliferation significantly. Prediction and annotation revealed that circ-DLG1 was able to sponge to 20 miRNAs and 60 corresponding target mRNAs.
Conclusion: Our study indicated that upregulation of circ-DLG1 promoted esophageal cell proliferation ability and might serve as a novel biomarker for ESCC.
Keywords: ESCC, spong, upregulation, biomarker, miRNA