108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

RAI14 的敲除可抑制胃癌进展
Authors Chen C, Maimaiti A, Zhang X, Qu H, Sun Q, He Q, Yu W
Received 27 May 2018
Accepted for publication 24 August 2018
Published 9 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6693—6703
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S175502
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Background: Retinoic acid induced 14 (RAI14 ), also known as NORPEG , is reported as being deregulated in non-small-cell lung cancer, together with having involvement in its cell proliferation as a super enhancer related gene.
Purpose: The objective of this study was to investigate the role of RAI14 in the progression and metastasis of gastric cancer and explore the associated mechanism.
Materials and methods: GEPIA database was used to analyze the expression of RAI14 in gastric cancer. MNK45 and AGS cells were transfected with siRNA-RAI14 to block the expression of RAI14 . Cell Counting Kit 8 and colony formation assays were performed to measure cell proliferation. Cell migration and invasion capacities was examined by transwell assay. Apoptosis rate was detected using flow cytometry, and the protein levels of apoptosis-related proteins was determined using Western blot assay. Reverse-transcription PCR assay was used to detect the expressions of RAB31 .
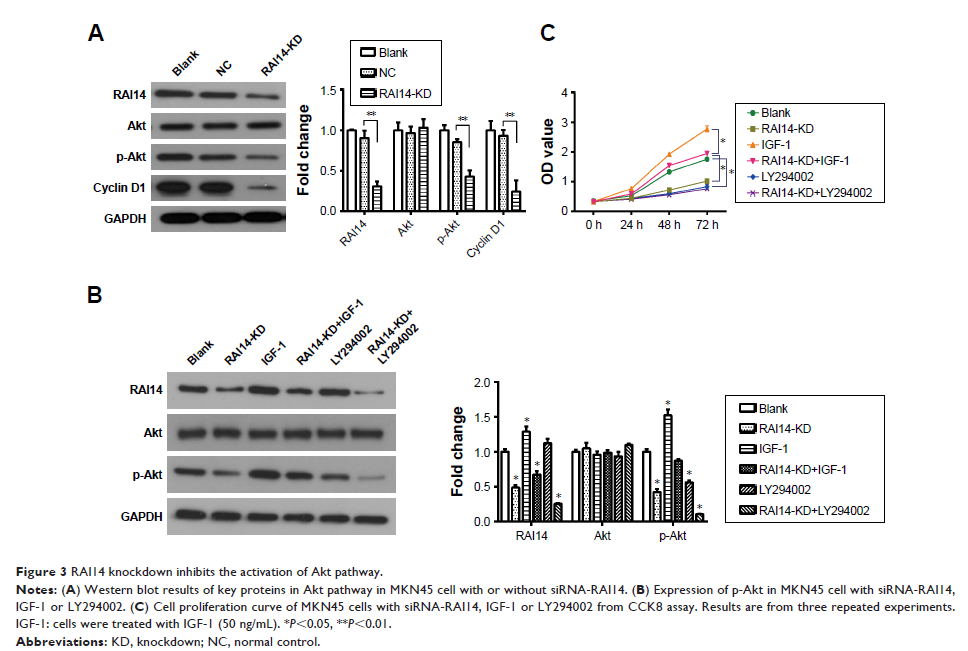
Results: Gene expression profiling interactive analysis revealed that RAI14 was substantially upregulated in gastric cancer and higher expression of RAI14 was associated with worse prognosis. We also observed that the knockdown of RAI14 by siRNA-RAI14 transfection suppressed growth capacity of MKN45 and AGS cells. Also, RAI14 knockdown inhibited migration and invasion of MKN45 and AGS cells in vitro. Moreover, RAI14 knockdown was observed to accelerate cell apoptosis via downregulation of Bcl-2 and upregulation of Bax in MKN45 and AGS cells. Furthermore, downregulation of RAI14 inhibited the activation of Akt pathway, and activation of Akt by IGF-1 could restore the reduced proliferation induced by RAI14 knockdown. In addition, we found that RAI14 had a positive correlation with the RAB31 in gastric cancer by GEPIA reverse-transcription PCR and Western blot assays, and the reduced proliferation caused by RAI14 knockdown was restored by RAB31 .
Conclusion: RAI14 knockdown inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion and promoted apoptosis by downregulating the Akt pathway in gastric cancer cells, and RAB31 might be a downstream target gene of RAI14 , providing a novel sight into the molecular mechanism of RAI14 and a potential target for gastric cancer treatment.
Keywords: RAI14 , gastric cancer, progression, Akt pathway, RAB31