108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

针对患有非小细胞肺癌的非吸烟女性,通过生物信息学分析进行基因鉴定和预后价值分析
Authors Yang GD, Chen QY, Xiao JM, Zhang HL, Wang ZC, Lin XG
Received 17 May 2018
Accepted for publication 24 August 2018
Published 8 October 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 4287—4295
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S174409
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: This study was performed to identify disease-related genes and analyze prognostic values in nonsmoking females with non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC).
Materials and methods: Gene expression profile GSE19804 was downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and analyzed by using GEO2R. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes were used for the functional and pathway enrichment analysis. Then, the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes, Cytoscape, and Molecular Complex Detection were used to construct the protein–protein interaction (PPI) network and identify hub genes. Finally, the Kaplan–Meier plotter online tool was used for the overall survival analysis of hub genes.
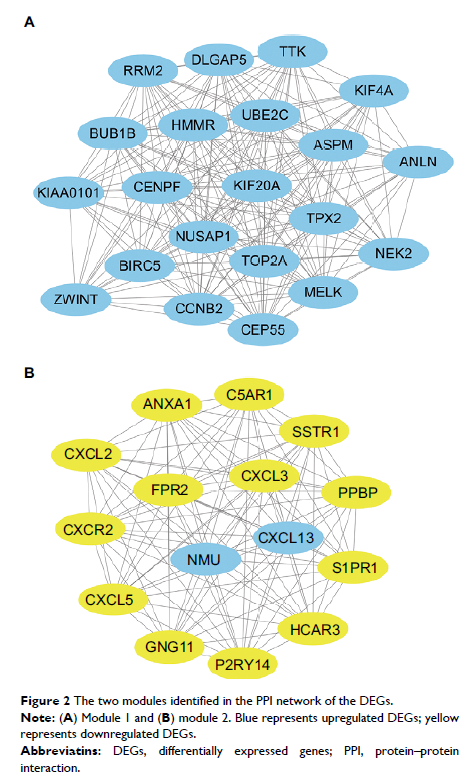
Results: A cohort of 699 differentially expressed genes was screened, and they were mainly enriched in the terms of ECM–receptor interaction, focal adhesion, and cell adhesion molecules. A PPI network was constructed, and 15 hub genes were identified base on the subset of PPI network. Then, two significant modules were detected and several genes were found to be associated with the cell cycle pathway. Finally, nine hub genes’ (UBE2C, DLGAP5, TPX2, CCNB2, BIRC5, KIF20A, TOP2A, GNG11, and ANXA1) expressions were found to be associated with the prognosis of the patients.
Conclusion: Overall, we propose that the cell cycle pathway may play an important role in nonsmoking females with NSCLC and the nine hub genes may be further explored as potential targets for NSCLC diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: non-small cell lung carcinoma, NSCLC, nonsmoking females, GEO2R, prognostic biomarkers, Kaplan–Meier plotter