108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

天冬酰胺合成酶表达与体外和体外结外自然杀伤/T 细胞淋巴瘤中的天冬酰胺酶敏感性有关
Authors Liu WJ, Wang H, Peng XW, Wang WD, Liu NW, Wang Y, Lu Y
Received 2 November 2017
Accepted for publication 6 August 2018
Published 8 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6605—6615
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S155930
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Faris Farassati
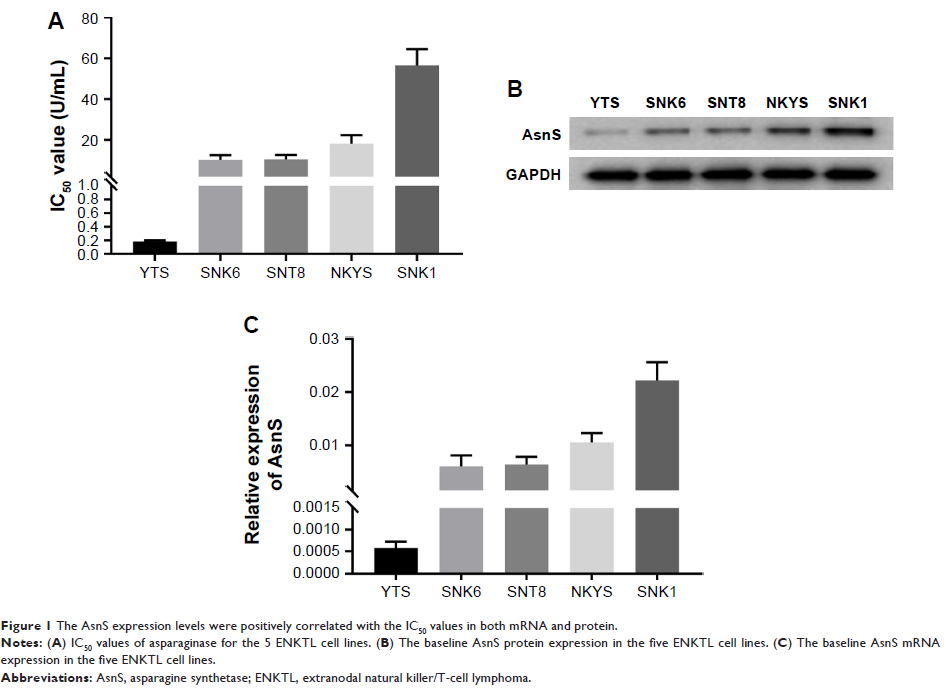
Background: Although asparagine synthetase (AsnS) is associated with drug resistance in leukemia, its function in extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL) remains unclear.
Methods: The present study investigated the relationship between baseline AsnS mRNA levels and response to asparaginase in ENKTL cell lines. It also determined whether upregulating or downregulating the AsnS mRNA level induces or reverses asparaginase-resistant phenotype.
Results: Interestingly, considerable differences were observed in the sensitivity to asparaginase of the five ENKTL cell lines. The AsnS expression levels were positively correlated with the IC50 values. In addition, the asparaginase resistance was induced or reversed by upregulating or downregulating the AsnS mRNA level in vivo and in vitro. Functional analyses indicated that AsnS did not affect the proliferation and apoptosis of ENKTL cells in the absence of asparaginase.
Conclusion: Together, the data stress the importance of AsnS in the sensitivity to asparaginase in ENKTL and suggest a different therapeutic strategy for patients with a different level of AsnS expression.
Keywords: asparagine synthetase, extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphomax, asparaginase resistance