108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

SERS 检测新策略用于以免疫识别和氧化石墨烯纳米带催化为基础的微量白蛋白尿定量分析
Authors Wen G, Jing Q, Liang A, Jiang Z
Received 20 May 2018
Accepted for publication 2 August 2018
Published 5 October 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 6099—6107
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S174765
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
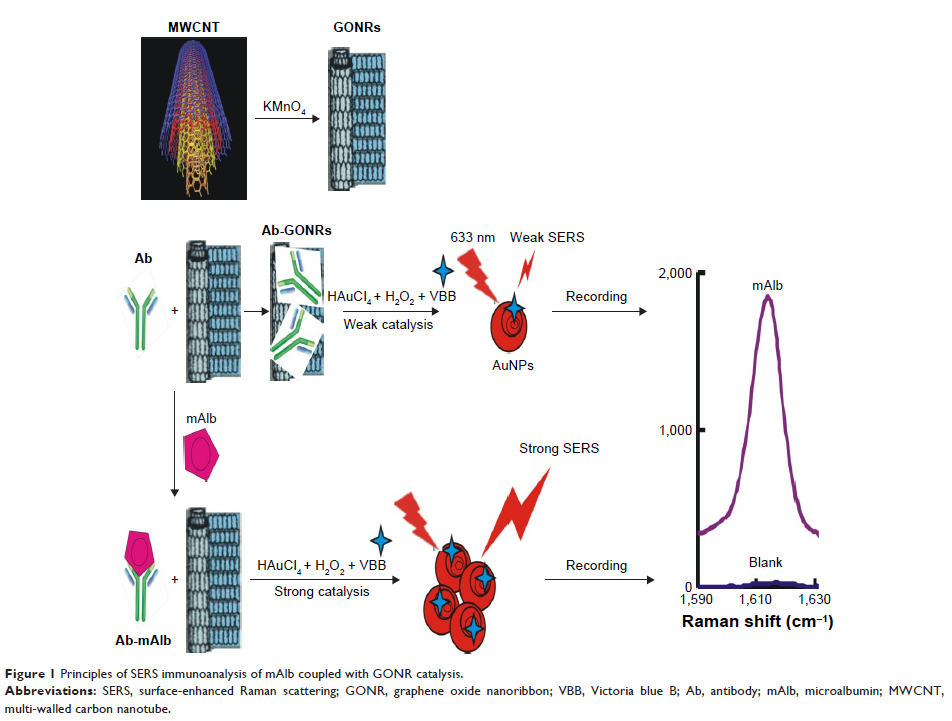
Background: Microalbuminuria (mAlb) detection is essential for the diagnosis and prognosis of nephrotic patients and hypoproteinemia. In this article, we develop a new surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) quantitative analysis method to detect mAlb in urine.
Methods: Combined the mAlb immunoreaction with gold nanoreaction of graphene oxide nanoribbons (GONR)-HAuCl4-H2O2, and used Victoria blue B (VBB) as molecular probe with a SERS peak at 1,615 cm-1, a new SERS strategy for quantitative analysis of trace mAlb in urine was established.
Results: The linear range of SERS quantitative analysis method is from 0.065 to 2.62 ng/mL, with a detection limit of 0.02 ng/mL. The SERS method was applied to analysis of mAlb in urine with good accuracy and reliability, the relative standard deviation is 0.49%–2.28% and the recovery is 96.9%–109.8%.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that the new SERS quantitative analysis method is of high sensitivity, good selectivity and simplicity. It has been applied to analysis of mAlb in urine, with satisfactory results.
Keywords: graphene oxide nanoribbon, nanocatalysis, microalbumin immunoreaction, gold nanoreaction, SERS