108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

RNF6 的敲除法通过遏制 STAT3 信号传导抑制胃癌细胞生长
Authors Huang Z, Cai Y, Yang C, Chen Z, Sun H, Xu Y, Chen W, Xu D, Tian W, Wang H
Received 21 May 2018
Accepted for publication 20 August 2018
Published 5 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6579—6587
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S174846
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
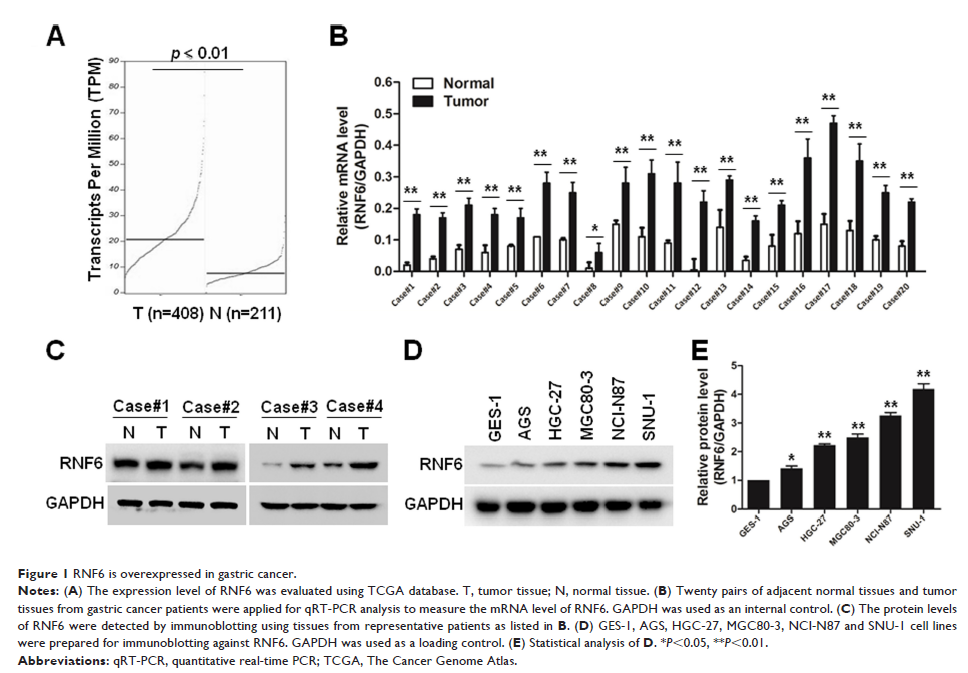
Background and objective: RNF6, an E3 ligase, has been reported to play an important role in the tumorigenesis in several tissues, but its role in gastric cancer is still unknown. In this study, we aimed to investigate the biological function and molecular mechanisms of RNF6 in gastric cancer.
Materials and methods: The expression levels of RNF6 were detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and immunoblotting in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines. Cell Counting Kit-8 assay was performed to evaluate cell proliferation. Cell apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometer and immunoblotting. Luciferase assay, immunoblotting and qRT-PCR were performed to explore the activation of STAT3. Immunoprecipitation was performed to evaluate the ubiquitination of SHP-1.
Results: In this study, RNF6 was found to be upregulated in both primary tissues and cell lines of gastric cancer. Knockdown or overexpression of RNF6 inhibited or promoted cell growth of gastric cancer cells. Knockdown of RNF6 also induced the cleavage of PARP and promoted cell apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. In addition, knockdown of RNF6 also increased the cytotoxicity of doxorubicin against gastric cancer. Moreover, knockdown of RNF6 inhibited STAT3-derived luciferase activity and downregulated the phosphorylation of STAT3, but upregulated the protein level of SHP-1. Knockdown of RNF6 downregulated the expression of MCL1 and XIAP, which are target genes of STAT3. Further studies showed that RNF6 regulated the stability of SHP-1 by inducing its polyubiquitination.
Conclusion: These results demonstrated that RNF6 was highly expressed in gastric cancer and regulated the growth of gastric cancer cells by affecting SHP-1/STAT3 signaling, which suggested that RNF6 could be a novel target for gastric cancer therapy.
Keywords: RNF6, cell growth, gastric cancer, STAT3, SHP-1