108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Nodal 通过 ALK/Smad 信号通路调节膀胱癌细胞迁移和侵袭
Authors Li Y, Zhong W, Zhu M, Hu S, Su X
Received 17 June 2018
Accepted for publication 30 August 2018
Published 5 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6589—6597
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S177514
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Background: Bladder cancer is the most common malignant tumor of the urinary tract. We aimed to explore the biological role and molecular mechanism of Nodal in bladder cancer.
Materials and methods: The expression of Nodal in bladder cancer tissues and cells was determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. The effect of silencing of Nodal on cell proliferation, clone formation, and migration and invasion was evaluated by MTT cell proliferation assay, colony formation, and transwell assays, respectively. Western blot analysis was employed to detect the expression of proliferation- and invasion-related proteins and proteins involved in ALK/Smad signaling.
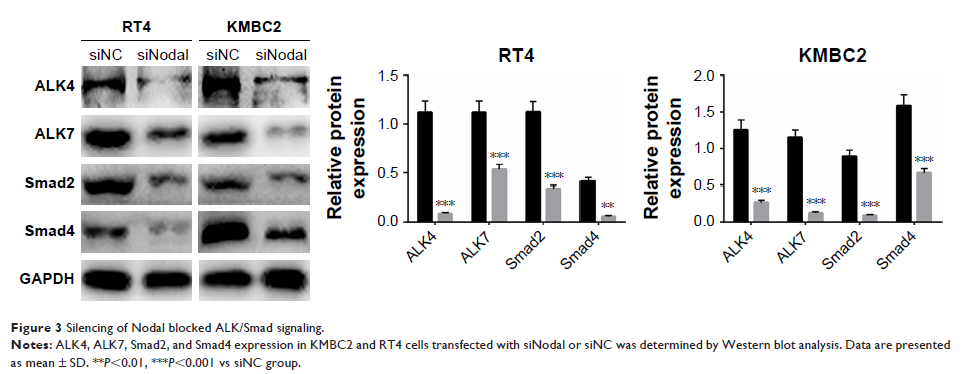
Results: We found that the expression of Nodal was significantly increased in bladder cancer tissues and cell lines. Downregulation of Nodal effectively weakened cell proliferation, clone formation, and cell migration and invasion abilities. The protein expression levels of CDC6, E-cadherin, MMP-2, and MMP-9 were also altered by downregulation of Nodal. Knockdown of Nodal also blocked the expression of ALK4, ALK7, Smad2, and Smad4, which are involved in ALK/Smad signaling. Additionally, the ALK4/7 receptor blocker SB431542 reversed the promotive effects of Nodal overexpression on bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion.
Conclusion: Our study indicated that Nodal functions as an oncogene by regulating cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in bladder cancer via the ALK/Smad signaling pathway, thereby providing novel insights into its role in bladder cancer treatment.
Keywords: bladder cancer, Nodal, migration, invasion, ALK4, Smad2