108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

布鲁氏菌 D 的自纳米乳化给药系统:抗溃疡性结肠炎的新方法
Authors Dou Y, Zhou J, Wang T, Huang Y, Chen VP, Xie Y, Lin ZX, Gao J, Su Z, Zeng H
Received 15 May 2018
Accepted for publication 2 August 2018
Published 28 September 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 5887—5907
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S174146
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Bruceine D (BD) is a major bioactive component isolated from the traditional Chinese medicinal plant Brucea javanica which has been widely utilized to treat dysentery (also known as ulcerative colitis [UC]).
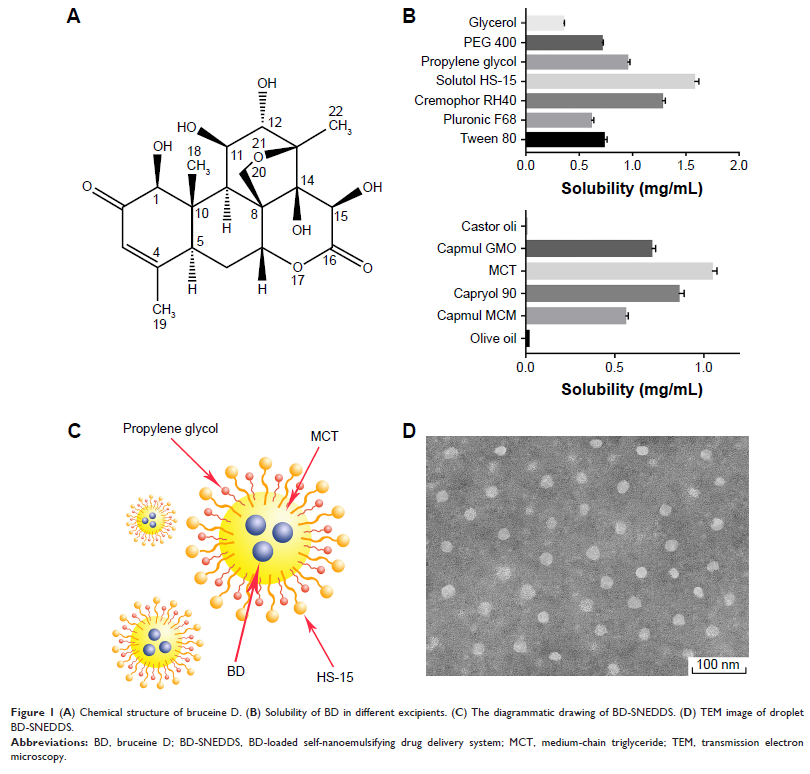
Methods: To improve the water solubility and absolute bioavailability of BD, we developed a self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) composing of MCT (oil), Solutol HS-15 (surfactant), propylene glycol (co-surfactant) and BD. The physicochemical properties and pharmacokinetics of BD-SNEDDS were characterized, and its anti-UC activity and potential mechanism were evaluated in TNBS-induced UC rat model.
Results: The prepared nanoemulsion has multiple beneficial aspects including small mean droplet size, low polydispersity index (PDI), high zeta potential (ZP) and excellent stability. Transmission electron microscopy showed that nanoemulsion droplets contained uniform shape and size of globules. Pharmacokinetic studies demonstrated that BD-SNEDDS exhibited enhanced pharmacokinetic parameters as compared with BD-suspension. Moreover, BD-SNEDDS significantly restored the colon length and body weight, reduced disease activity index (DAI) and colon pathology, decreased histological scores, diminished oxidative stress, and suppressed TLR4, MyD88, TRAF6, NF-κB p65 protein expressions in TNBS-induced UC rat model.
Conclusion: These results demonstrated that BD-SNEDDS exhibited highly improved oral bioavailability and advanced anti-UC efficacy. In conclusion, our current results provided a foundation for further research of BD-SNEDDS as a potential complementary therapeutic agent for UC treatment.
Keywords: bruceine D, self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system, physicochemical properties, pharmacokinetics, anti-inflammation, anti-colitis activity