108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

健康教育有助于缓解肝动脉化疗栓塞术期间的栓塞后疼痛
Authors Wang ZX, Li L, Tao FY
Received 23 February 2018
Accepted for publication 14 August 2018
Published 28 September 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2115—2121
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S166333
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Katherine Hanlon
Aim: Psychological intervention has been proved a complementary approach to drug analgesia. Another study suggested that health knowledge is associated with psychological symptoms in patients with liver cancer. This study is conducted to assess whether improving the health education (HE) alleviates the postembolization pain during transarterial chemoembolization (TACE).
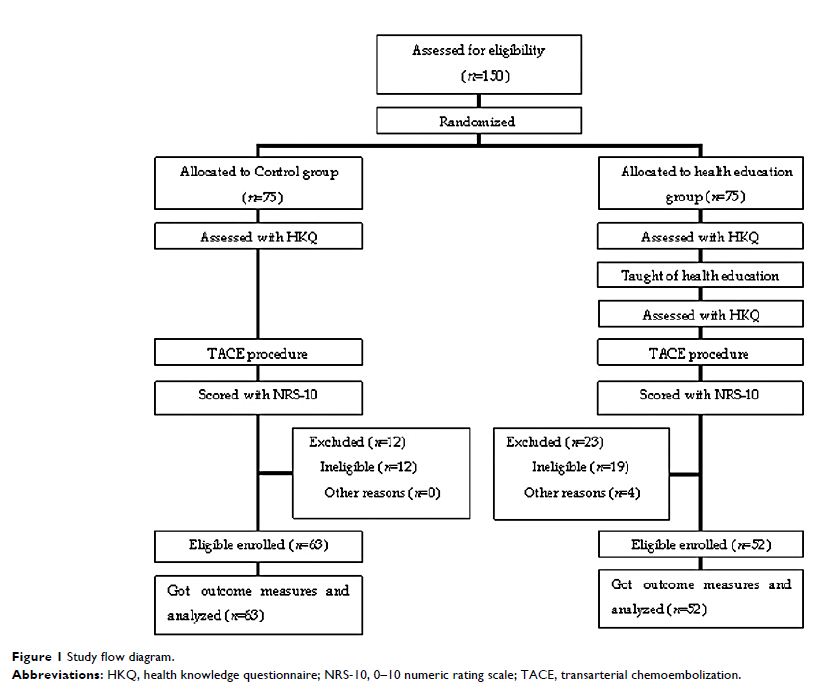
Materials and methods: One hundred and fifteen patients, who required TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and suffered postembolization pain, were randomized into control group (n=63) and HE group (n=52). The health knowledge was scaled with the health knowledge questionnaire (HKQ). The postembolization pain was scored using a 0–10 numeric rating scale (NRS-10) after arterial embolization in both groups.
Results: There were no statistical differences between male and female in all HKQ scores (P >0.05). The HKQ scores of young people (≤45 years old) were significantly higher than those of elders (>45 years old; P <0.05). After teaching HE, the HKQ scores were significantly increased in patients of the HE group (P <0.01). The postembolization pain score in the HE group was significantly lower than that in the control group (P <0.05). The HKQ scores of question 1, 3, and total were negatively correlated with the pain score in this sample (P <0.05).
Conclusion: Improving the HE among HCC patients before TACE is beneficial for the pain relief during interventional procedure.
Keywords: liver neoplasms, radiology, health education, non-pharmacological, pain