108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

微卫星的不稳定性与 BRAF 突变相结合对于结直肠癌的预后价值
Authors Yang Y, Wang D, Jin L, Wu G, Bai Z, Wang J, Yao H, Zhang Z
Received 29 March 2018
Accepted for publication 9 July 2018
Published 26 September 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 3911—3929
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S169649
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Kenan Onel
Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic value of the combination of microsatellite instability (MSI) and BRAF V600E mutation in colorectal cancer (CRC).
Materials and methods: We compare the prognosis difference among CRC patients with four subtypes according to MSI and BRAF mutation, ie, microsatellite stable/BRAF wild type (MSS/BRAF wt), MSS/BRAF mutation (MSS/BRAF mut), MSI/BRAF wt, and MSI/BRAF mut, by pooling the previous related reports and public available data sets till December 2017 for the first time.
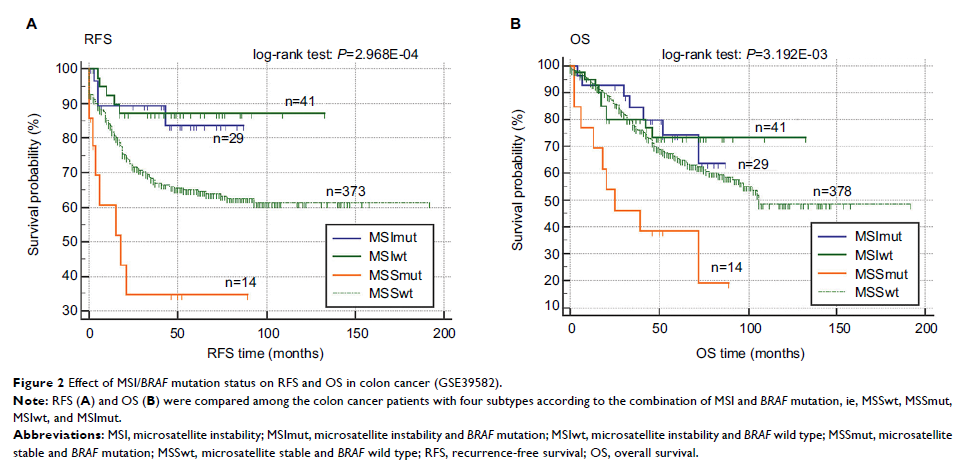
Results: Twenty-seven independent studies comprising 24,067 CRC patients were included. Meta-analysis suggested that, compared with MSS/BRAF wt subtype, MSS/BRAF mut was associated with shorter overall survival (OS) (N=25, HR = 2.018, 95% CI = 1.706–2.388, P =2.220E-16), while there was a trend of association of MSI/BRAF mut with OS (N=13, HR = 1.324, 95% CI = 0.938–1.868, P =1.096E-01) and no association of MSI/BRAF wt with OS (N=17, HR = 0.996, 95% CI = 0.801–1.240, P =9.761E-01). Compared with MSI/BRAF wt subtype, MSI/BRAF mut was a poor factor for OS (N=22, HR = 1.470, 95% CI = 1.243–1.740, P =7.122E-06). Compared with MSS/BRAF mut subtype, both MSI/BRAF wt (N=11, HR = 0.560, 95% CI = 0.433–0.725, P =1.034E-05) and MSI/BRAF mut (N=16, HR = 0.741, 95% CI = 0.567–0.968, P =2.781E-02) were favorable for OS. Subgroup analysis revealed similar results in all subgroups except the subgroup of stage IV cancer, in which MSI showed poor effects on OS in BRAF wild-type patients (N=6, HR = 1.493, 95% CI = 1.187–1.879, P =6.262E-04) but not in BRAF -mutated patients (N=5, HR = 1.143, 95% CI = 0.789–1.655, P =4.839E-01). Meta-analysis regression and test of interaction revealed no interaction of MSI with BRAF mutation when evaluating the associations of MSI/BRAF mutation subtypes with OS in CRC.
Conclusion: Among the four subtypes according to MSI and BRAF mutation, MSS/BRAF mut was a poor prognostic factor, while MSS/BRAF wt and MSI/BRAF wt were comparable and favorable and MSI/BRAF mut was moderate in CRC. The combination of MSI/BRAF mutations could facilitate the planning of individualized treatment strategies and prognosis improvement in CRC.
Keywords: meta-analysis, microsatellite instability, colorectal cancer, BRAF mutation, prognosis