108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

附着在主要血管的肝内胆管细胞癌患者接受狭窄边缘肝切除术后进行辅助放疗的益处
Authors Zheng X, Chen B, Wu JX, Jia AY, Rong WQ, Wang LM, Wu F, Zhao YT, Li YX, Wang WH
Received 3 May 2018
Accepted for publication 23 July 2018
Published 26 September 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 3973—3981
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S172940
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Purpose: To evaluate the role of adjuvant radiotherapy after narrow-margin (<1.0 cm) resection in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) adherent to major vessels.
Patients and methods: This retrospective study included 70 ICC patients. Forty-nine patients received narrow-margin (<1.0 cm) hepatectomy and 21 patients underwent wide-margin (≥1.0 cm) hepatectomy (Group C). Twenty-six of 49 were treated with postoperative radiotherapy (Group A), while the remaining 23 did not receive radiotherapy (Group B). Clinical outcomes were compared in the 3 groups. Toxicities of radiotherapy were evaluated.
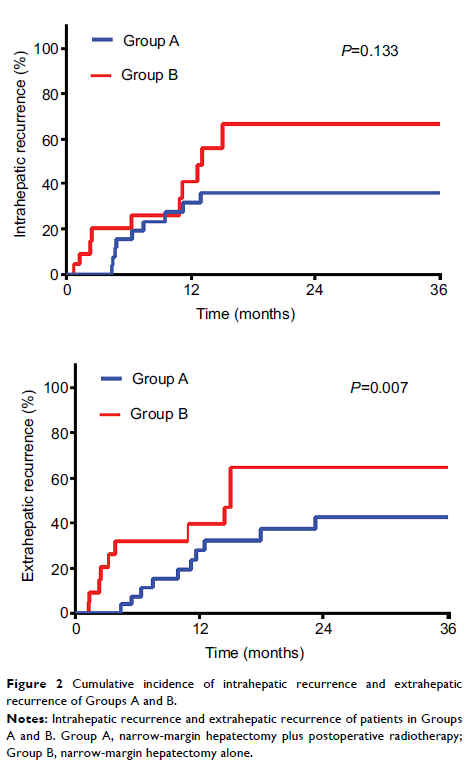
Results: With a median follow-up time of 42 months, the 3-year overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival rates were 55% and 44% for Group A, 20% and 10% for Group B, and 65% and 33% for Group C, respectively. The OS and disease-free survival in Groups A and C were comparable and improved compared to Group B (Group A vs B, P =0.011 and P =0.031; and Group C vs B, P =0.031 and P =0.105). Multivariate analysis showed that receiving narrow-margin resection only (adjusted hazard ratio: 3.73; 95% CI: 1.36–10.25; P =0.001) was a significant poor prognostic risk factor of OS. Group B experienced more intrahepatic recurrence and extrahepatic recurrence than Groups A and C. For Groups A and B, the 3-year intrahepatic recurrence rates were 36% vs 67% (P =0.133) and extrahepatic recurrence rates were 43% vs 65% (P =0.007). Only 2 patients in Group A suffered from grade 3 toxicities. No patient developed classic or nonclassic radiation-induced liver disease.
Conclusion: Postoperative radiotherapy following narrow-margin hepatectomy seems to be efficacious and well-tolerated in patients with ICC adjacent to major vessels.
Keywords: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, surgical margin, hepatectomy, surgery, postoperative radiotherapy, prognosis