108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

全反式维甲酸包裹、CD20 抗体偶联的聚(乳酸 - 共- 羟基乙酸)纳米粒子有效地靶向并在体外消除黑素瘤起始细胞
Authors Chen X, Zhang Z, Yang S, Chen H, Wang D, Li J
Received 2 April 2018
Accepted for publication 12 August 2018
Published 25 September 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6177—6187
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S169957
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Purpose: Melanoma, which is initiated from melanocytes, is the most fatal type of skin cancer. Melanoma-initiating cells significantly contribute to the initiation, metastasis, and recurrence of melanoma, and CD20 is a marker of melanoma-initiating cells. All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) has been demonstrated to induce differentiation, inhibit proliferation, and promote the apoptosis of cancer cells and cancer-initiating cells (CICs). However, there has been no report on ATRA activity against melanoma-initiating cells. In this study, we examined the activity of ATRA against melanoma-initiating cells and developed ATRA-encapsulated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles, which were conjugated with a CD20 antibody (ATRA-PNP-CD20) for targeted delivery of ATRA to CD20+ melanoma-initiating cells.
Materials and methods: The effects of ATRA and ATRA-PNP-CD20 against melanoma-initiating cells were investigated using a cytotoxicity assay, tumorsphere formation assay, and flow cytometry.
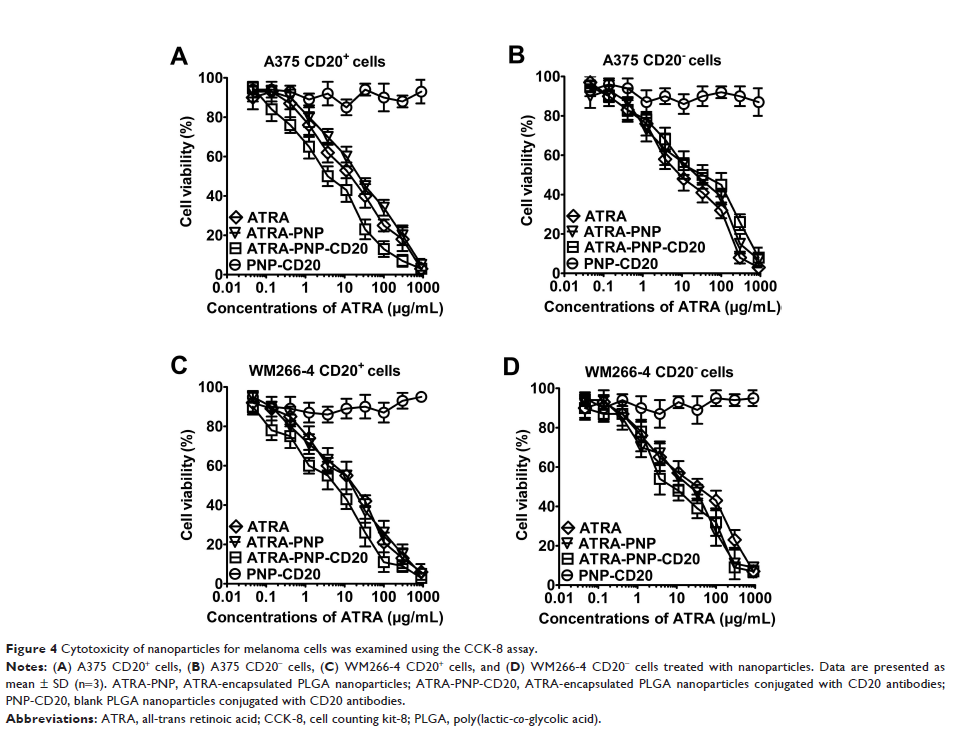
Results: ATRA-PNP-CD20 had a size of 126.9 nm and a negative zeta potential. The drug-loading capacity of ATRA-PNP-CD20 was 8.7%, and ATRA-PNP-CD20 displayed a sustained release of ATRA for 144 hours. The results showed that ATRA-PNP-CD20 could effectively and specifically deliver ATRA to CD20+ melanoma-initiating cells, achieving superior inhibitory effects against CD20+ melanoma-initiating cells compared with those of free ATRA and nontargeted nanoparticles. To the best of our knowledge, we report for the first time a potent activity of ATRA against CD20+ melanoma-initiating cells, targeted drug delivery of ATRA via nanoparticles to melanoma-initiating cells, and the achievement of a superior inhibitory effect against melanoma-initiating cells by using a CD20 antibody.
Conclusion: ATRA-PNP-CD20 represents a promising tool for eliminating melanoma-initiating cells and shows a potential for the therapy of melanoma.
Keywords: melanoma, cancer-initiating cells, nanoparticles, CD20, antibody