108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PLK1 通过 PDTX 模型上的 MEK-ERK 途径可成为胃癌的潜在预后标志物
Authors Dang SC, Fan YY, Cui L, Chen JX, Qu JG, Gu M
Received 1 April 2018
Accepted for publication 11 July 2018
Published 25 September 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6239—6247
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S169880
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
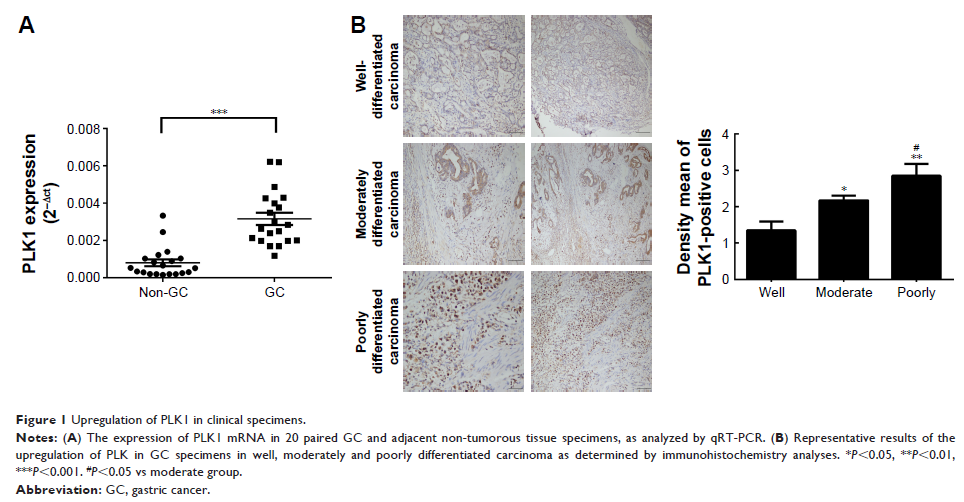
Background: PLK1 has been identified as having a great effect on cell division and maintaining genomic stability in mitosis, spindle assembly, and DNA damage response by current studies.
Materials and methods: We assessed PLK1 expression in cervical cancer tissues and cells. We have also evaluated the effects of PLK1 on gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis both in vitro and in vivo.
Results: Our results show that PLK1 is overexpressed in gastric cancer tissues and cells. Inhibition of PLK1 contributes cell cycle G2-phase arrest and inhibits the proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of gastric cancer (GC) cells, whereas its overexpression promotes proliferation, migration, and apoptosis in these cells. Moreover, PLK1 inhibition reduces expression of pMEK and pERK. More importantly, in vivo by analyzing tumorigenesis in patient-derived tumor xenograft (PDTX) models, the inhibition of PLK1 activity by BI6727 significantly decreased the volume and weight of the tumors compared with control group (P <0.01).
Conclusion: Our results found that PLK1 has a significant impact on the survival of GC cells; it may become a prognostic judge, a potential therapeutic target, and a preventative biomarker of GC.
Keywords: gastric cancer, PLK1, cell cycle, apoptosis, MEK/ERK pathway, patient-derived tumor xenografts