108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

预测肺腺癌特异性生存率的表达特征模型
Authors Shi X, Tan H, Le X, Xian H, Li X, Huang K, Luo VY, Liu Y, Wu Z, Mo HY, Chen AM, Liang Y, Zhang J
Received 11 December 2017
Accepted for publication 9 April 2018
Published 24 September 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 3717—3732
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S159563
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Luzhe Sun
Background: The current TNM staging system plays a central role in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) prognosis. However, it may not adequately stratify the risk of tumor recurrence. With the aid of gene expression profiling, we identified 31 lncRNAs whose expressions in tumor tissues could be used as a risk indicator for the guidance of lung cancer therapy. This exploratory analysis may shed new light on identification of potential prognostic factors.
Materials and methods: A survival prediction scoring model was developed from the data that are publicly available in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) LUAD RNA Sequencing dataset. Multivariate Cox regression analysis and Kaplan–Meier analysis were performed on a cohort of 254 stage I lung carcinoma patients with survival records.
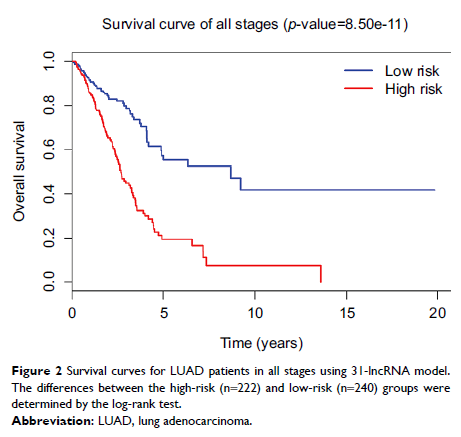
Results: Our model indicates that the panels comprising 31 lncRNAs are highly associated with overall survival (OS): 18.9% (95% CI: 10.4%–34.5%) and 89.5% (95% CI: 80.7%–99.2%) for the high- and low-risk group, respectively. The specificity and sensitivity of the model are verified, which show that the area under receiver operating characteristic curve yields 0.881, meaning our model has good accuracy and it is feasible for further applications.
Conclusion: The 31-lncRNA model might be able to predict OS in patients with LUAD with high accuracy. Its further applications in biomolecular experiments using clinical samples with independent cohorts of patients are needed to verify the results.
Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma, lncRNA, signature, survival analysis, prognosis, RNA-seq