108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

胃癌联合治疗:透明质酸和含有脂质前药的顺铂结合,同时在纳米颗粒系统中加载索拉非尼,以显示出增强的抗癌功效和降低的毒性
Authors Yang F, Li A, Liu H, Zhang H
Received 11 June 2018
Accepted for publication 1 September 2018
Published 4 October 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 3321—3333
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S176879
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Manfred Ogris
Purpose: Gastric cancer is one of the most common human epithelial malignancies,
and using nanoparticles (NPs) in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer has been
extensively studied. The aim of this study was to develop hyaluronic acid (HA)
containing lipid NPs coloaded with cisplatin (CDDP) and sorafenib (SRF) for the
treatment of gastric cancer.
Materials and
methods: HA and CDDP containing lipid prodrug
was synthesized using polyethylene glycol (PEG) as a linker (HA-PEG-CDDP).
HA-PEG-CDDP and SRF were entrapped into the lipid NPs by nanoprecipitation
method (H-CS-NPs). The physicochemical and biochemical properties such as size,
zeta potential, and drug release pattern were studied. In vitro viability was
also evaluated with MKN28 and SGC7901 human gastric cancer cells. In vivo
testing including biodistribution and accumulation in tumor tissue was applied
in gastric tumor-bearing mice to confirm the inhibition of gastric cancer.
Results: H-CS-NP has a particle size of 173.2±5.9 nm, with a zeta potential
of -21.5±3.2 mV. At day 21 of in vivo treatment, H-CS-NPs inhibited the tumor
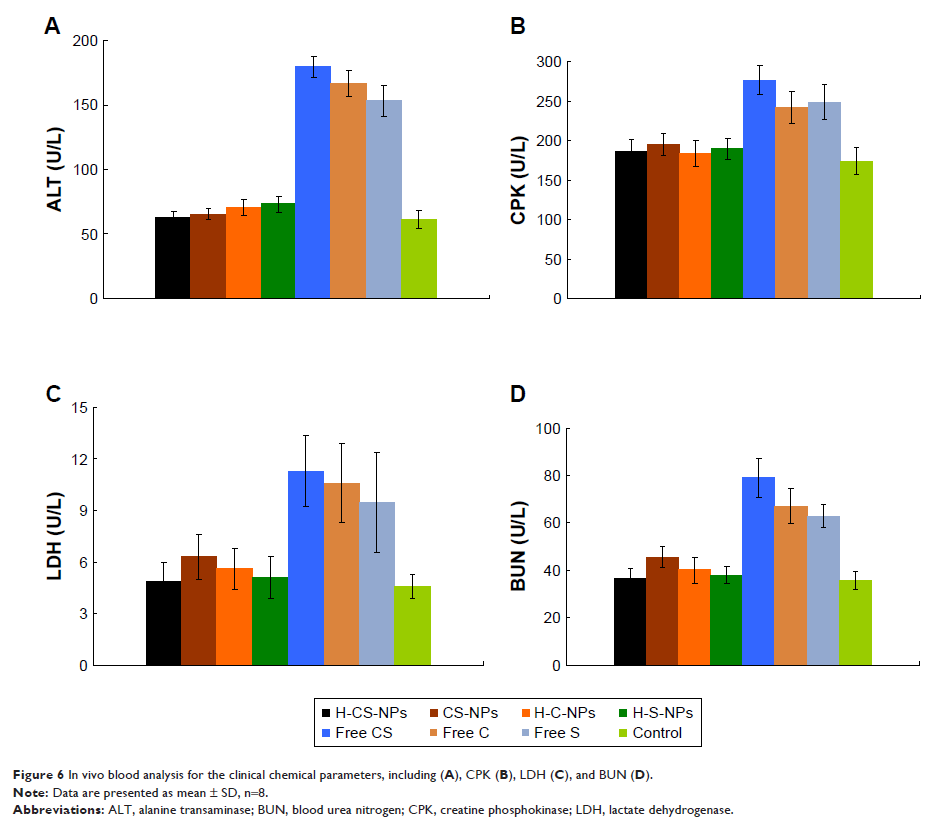
volume from 1,532.5±41.3 mm3 to 259.6±16.3 mm3 with no obvious body weight loss. In contrast, mice treated with
free drugs had body weight loss from 20 to 15 g at the end of study.
Conclusion: The results indicate that H-CS-NPs enhanced the antitumor effect of
drugs and reduced the systemic toxicity effects. It could be used as a
promising nanomedicine for gastric cancer combination therapy.
Keywords: nanocarriers, chemotherapy, polyethylene glycol, enhanced
permeability and retention effect, reticuloendothelial system