108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

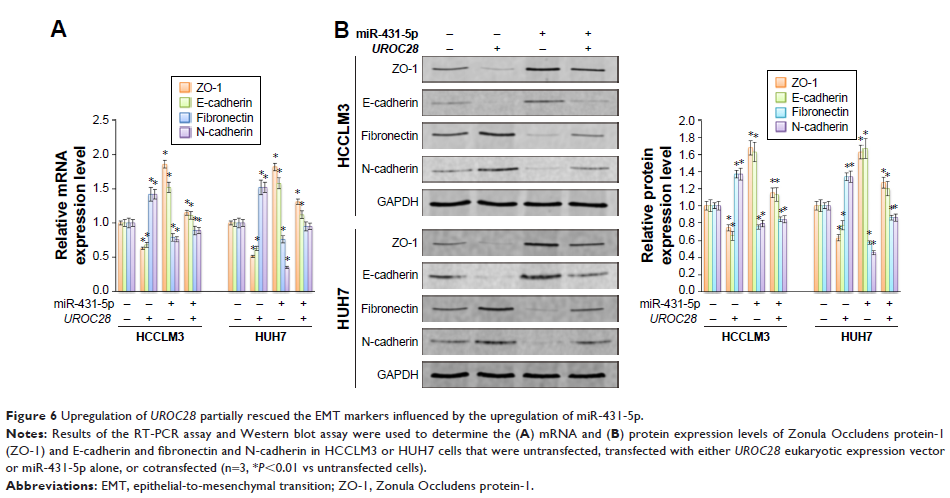
miR-431-5p 通过靶向肝癌细胞中的 UROC28 改变上皮 - 间充质转换标志物
Authors Kong Q, Han J, Deng H, Wu F, Guo S, Ye Z
Received 11 May 2018
Accepted for publication 20 August 2018
Published 4 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6489—6503
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S173840
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Objective: MicroRNA (miR)-431 plays an essential role in various human cancer
types, particularly in the process of invasion. However, the function and
mechanism of miR-431-5p in the invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
remain undefined.
Methods: The expression levels of miR-431-5p and its potential target
protein UROC28 in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells and tissues were detected, and the levels of EMT markers in
vivo and in vitro were also detected.
Results: MiR-431-5p was downregulated in HCC cell lines and tissues and
associated with vascular invasion and tumor encapsulation. Furthermore,
miR-431-5p was able to influence the epithelialto- mesenchymal transition (EMT)
process in HCCLM3 and HUH7 cells. Mechanistically, it was discovered that
miR-431-5p repressed invasion by targeting UROC28 .
Furthermore, miR-431-5p influenced the EMT markers in HCCLM3 and HUH7 cells by
downregulating UROC28 expression.
Similarly, in vivo assays confirmed that miR-431-5p upregulation in HCC cells
remarkably inhibited tumor proliferation and influenced the EMT markers.
Conclusion: The current study has demonstrated that the miR-431-5p/UROC28 axis acts possible
influence on the EMT in HCC. Upregulation of miR-431-5p could be an original
approach for inhibiting tumor invasion.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, microRNA-431, UROC28 , PBOV1, epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition