108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过采用术后强化恢复来降低住院费用和术后鼻中隔疼痛
Authors Liao ZP, Liao W, Tan KS, Sun YQ, Peng AQ, Zhu YX, He HX, Yang SW, Xu GF, Su RF, Yao JY, Fan YP, Yang QT, Hong HY
Received 10 May 2018
Accepted for publication 24 July 2018
Published 4 October 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 1871—1877
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S173687
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Hoa Le
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Objective: Septoplasty has been the definitive treatment for nasal septum
deviation, but its postoperative procedure may affect patients’ quality of
life. While new procedures in general surgery, such as enhanced recovery after
surgery (ERAS), can speed up postoperative rehabilitations to improve quality
of life, it is rarely applied in the ear–nose–throat field. This study
therefore aims to evaluate the application of ERAS in patients with nasal
septum deviation as a means of improving perioperative outcomes.
Materials and
methods: Fifty patients with nasal septum
deviation undergoing septoplasty were randomized as ERAS or control group (25
patients in both groups). Patients were investigated for outcomes including
length of stay, operating time, bleeding volume, total cost, complications, and
Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) and visual analog symptom score of nasal
obstruction, sleep disturbance, and head facial pain.
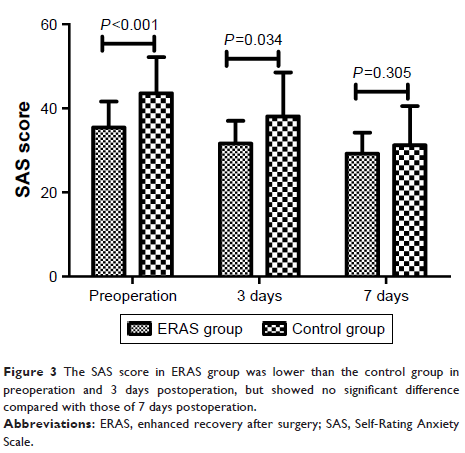
Results: The preoperative anxiety in ERAS group (SAS 35.4±6.2) was lower
than the control group (SAS 43.6±8.6). The anxiety levels in ERAS group (SAS
31.6±5.4) was also reduced compared to the control group (SAS 38.1±10.4) in the
3 days postsurgery, but showed no significant difference thereafter at 7 days
postsurgery. In addition, the length of stay and total cost were significantly
lower for the ERAS group as well. The visual analog symptom score of nasal
obstruction, sleep disturbance, and head facial pain in ERAS group were all
also found to be lower than the control group. The only outcomes with no
significant differences were the operation time, blood volume, and
complications between the groups.
Conclusion: Our study indicated ERAS application can reduce hospital charges
and postoperative pain in septoplasty, thereby improving patient quality of
life and hospital expenses at the same time.
Keywords: enhanced recovery after surgery, hospital charges, nasal septum
deviation, postoperative pain, septoplasty