108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过靶向人乳头瘤病毒的晚期和早期蛋白,设计 CD8+ 和 CD8+ 重叠的 CD4+ 表位疫苗
Authors Kaliamurthi S, Selvaraj G, Kaushik AC, Gu KR, Wei DQ
Received 21 June 2018
Accepted for publication 1 August 2018
Published 2 October 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 107—125
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/BTT.S177901
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Doris Benbrook
Background and
aim: Human papillomavirus (HPV) is an
oncogenic agent that causes over 90% of cases of cervical cancer in the world.
Currently available prophylactic vaccines are type specific and have less
therapeutic efficiency. Therefore, we aimed to predict the potential
species-specific and therapeutic epitopes from the protein sequences of HPV45
by using different immunoinformatics tools.
Methods: Initially, we determined the antigenic potential of late (L1 and
L2) and early (E1, E2, E4, E5, E6, and E7) proteins. Then, major
histocompatibility complex class I-restricted CD8+ T-cell epitopes were selected based on their immunogenicity. In
addition, epitope conservancy, population coverage (PC), and target
receptor-binding affinity of the immunogenic epitopes were determined.
Moreover, we predicted the possible CD8+, nested interferon gamma (IFN-γ)-producing CD4+, and linear B-cell epitopes. Further, antigenicity, allergenicity,
immunogenicity, and system biology-based virtual pathway associated with
cervical cancer were predicted to confirm the therapeutic efficiency of
overlapped epitopes.
Results: Twenty-seven immunogenic epitopes were found to exhibit cross-protection
(≥55%) against the 15 high-risk HPV strains (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 51, 52,
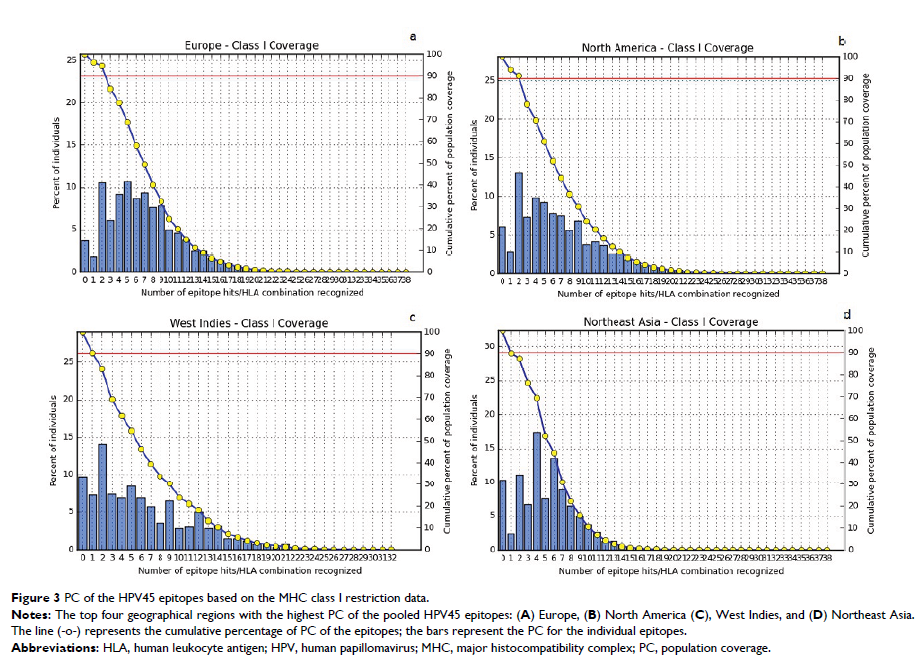
56, 58, 59, 68, 69, 73, and 82). The highest PC was observed in Europe
(96.30%), North America (93.98%), West Indies (90.34%), North Africa (90.14%),
and East Asia (89.47%). Binding affinities of 79 docked complexes observed as
global energy ranged from -10.80 to -86.71 kcal/mol. In addition, CD8+ epitope-overlapped segments in CD4+ and B-cell epitopes demonstrated that immunogenicity and
IFN-γ-producing efficiency ranged from 0.0483 to 0.5941 and 0.046 to 18,
respectively. Further, time core simulation revealed the overlapped epitopes
involved in pRb, p53, COX-2, NF-X1, and HPV45 infection signaling pathways.
Conclusion: Even though the results of this study need to be confirmed by
further experimental peptide sensitization studies, the findings on immunogenic
and IFN-γ-producing CD8+ and overlapped epitopes provide new insights into HPV vaccine
development.
Keywords: human leukocyte antigen, killer cells, overlapped epitopes, time
course simulation