108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

自噬对放射抗拒性的人鼻咽癌细胞株 CNE-2R 放射敏感性的作用
Authors Liang ZG, Lin GX, Yu BB, Su F, Li L, Qu S, Zhu XD
Received 7 June 2018
Accepted for publication 10 August 2018
Published 2 October 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 4125—4134
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S176536
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Purpose: The present study aimed to study the role of autophagy in the radiosensitivity
of the radioresistant human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE-2R.
Methods: Before being irradiated, CNE-2R cells were treated with the
autophagy inhibitor chloroquine diphosphate (CDP) or the autophagy inducer
rapamycin (RAPA). Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 (LC3-II) and p62
were assessed using Western blotting analysis 48 hours after CNE-2R cells were
irradiated. The percentage of apoptotic cells was assessed via flow cytometry.
CNE-2R cell viability was evaluated using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8). The
radiosensitivity of cells was assessed via clone formation analysis.
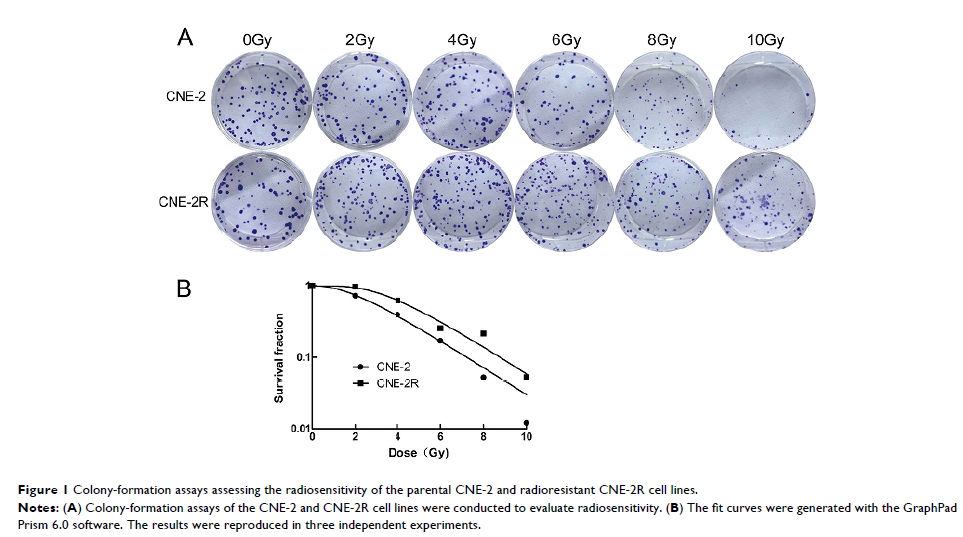
Results: The level of autophagy in CNE-2R cells improved as the radiation
dose increased, reaching the maximum at a dose of 10 Gy. Autophagy was most significantly
inhibited by 60 µmol/L CDP in CNE-2R cells, but was obviously enhanced by 100
nmol/L RAPA. Compared with the irradiation (IR) alone group, in the IR + CDP
group, autophagy was significantly inhibited, viability was low, the rate of
radiation-induced apoptosis was increased, and radiosensitivity was
upregulated. In contrast, cells of the IR + RAPA group exhibited greater
autophagy, higher viability, a lower rate of radiation-induced apoptosis, and
downregulated radiosensitivity.
Conclusion: The autophagy level is negatively correlated with radiosensitivity
for the radioresistant human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE-2R.
Keywords: nasopharyngeal carcinoma, autophagy, radiosensitivity