108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

cT1-2N0-1 期乳腺癌新辅助化疗后局部复发相关因素和风险适应性乳房切除术后放疗
Authors Wang X, Xu L, Yin Z, Wang D, Wang Q, Xu K, Zhao J, Zhao L, Yuan Z, Wang P
Received 9 May 2018
Accepted for publication 28 June 2018
Published 2 October 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 4105—4112
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S173628
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Objective: In order to identify risk factors associated with locoregional
recurrence (LRR) and assess the role of postmastectomy radiotherapy (PMRT) in
early breast cancer (BC), managed with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and
mastectomy, a retrospective analysis of BC diagnosed with clinical stage
T1-2N0-1 was conducted.
Patients and
methods: A total of 217 patients were
included in this analysis. The median age was 50 years (24–72 years). The
clinical stage distributions were cT1 in 15 cases, cT2 in 202, cN0 in 53, and
cN1 in 161 cases. All patients were treated with NAC and mastectomy, and 128
patients received PMRT.
Results: With a median follow-up time of 61 months, the 5-year cumulative
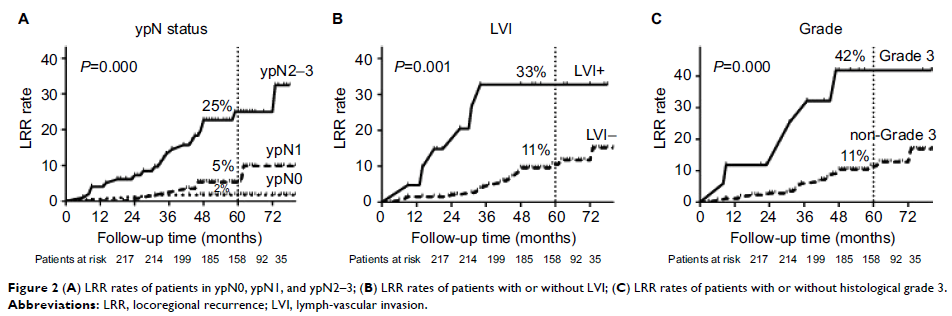
LRR rate was 12%. Multivariate analysis demonstrated that pathological N stage,
lymph-vascular invasion, and histological grade were independent prognostic
factors associated with LRR. A nomogram model based on these factors was
established, based on which the patients were deeply stratified into low- and
high-risk group. In the low-risk group, radiotherapy did not decrease LRR (3.3%
in PMRT group, 1.7% in no PMRT group, P =0.192). While in
the high-risk group, PMRT significantly decreased LRR (21.8% in PMRT group,
42.2% in no PMRT group, P =0.031).
Conclusion: Lymph-vascular invasion, histological grade, as well as
pathological N stage were important prognostic factors associated with LRR in
BC patients staged in cT1-2N0-1, who were managed with NAC and mastectomy. In
our cohort, not only clinical and pathological stage information but also other
risk factors were taken into consideration when adjuvant PMRT was recommended.
In the high-risk subgroup, PMRT significantly improved the prognosis.
Keywords: breast cancer, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, postmastectomy
radiotherapy, prognosis