108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LINC00460 通过靶向胃癌中的 miR-342-3p 来调节 KDM2A,以促进细胞增殖和迁移
Authors Wang F, Liang S, Liu X, Han L, Wang J, Du Q
Received 26 March 2018
Accepted for publication 26 May 2018
Published 2 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6383—6394
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S169307
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Background: Increasing evidence has shown that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs)
play important roles in the occurrence and development of human cancers.
LINC00460, a novel tumor-related lncRNA, has been reported to be involved in
several types of human malignancies. However, the role of LINC00460 in gastric
cancer (GC) is still unclear. The present study aimed at exploring the
biological role of LINC00460 in GC and illuminating the potential molecular
mechanisms.
Methods: In this study, qRT-PCR, western blotting, MTT assay, and Transwell
invasion assay were used to conduct relevant experimental analysis.
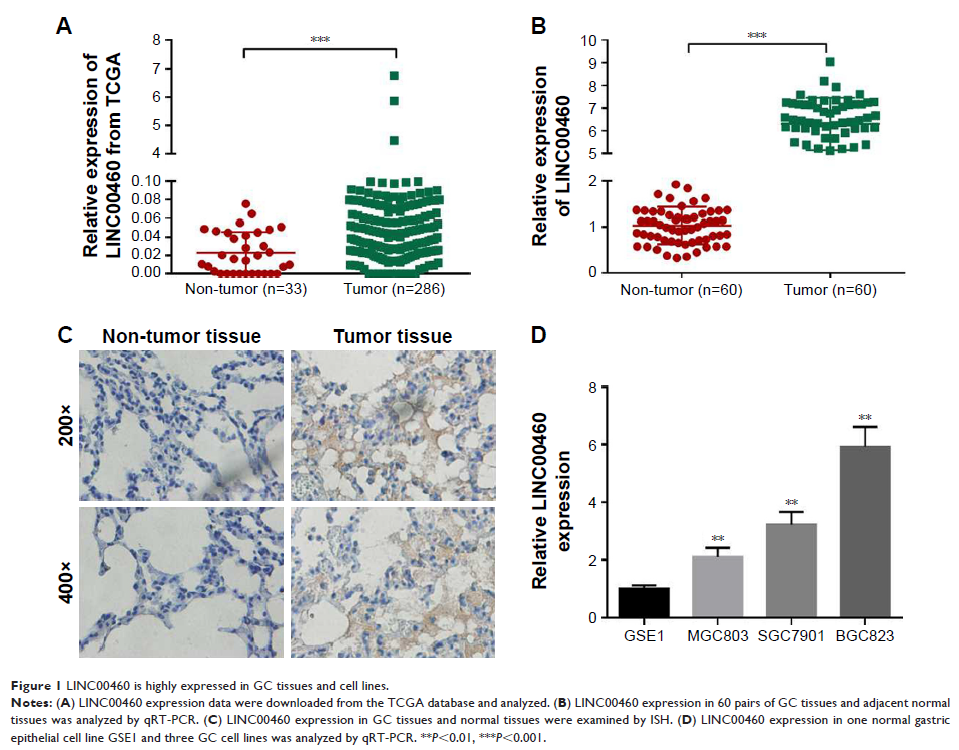
Results: Here, we found that LINC00460 was highly expressed in GC tissues
and cell lines. Moreover, LINC00460 over-expression was found to promote GC
cell proliferation, migration and invasion, whereas LINC00460 down-regulation
significantly inhibited these processes. Notably, we confirmed that LINC00460
could up-regulate KDM2A expression by competitively binding to miR-342-3p in GC
cells. Furthermore, the suppressive effects of LINC00460 down-regulation on GC
cell proliferation, migration and invasion were partially reversed by a
miR-342-3p inhibitor.
Conclusion: In summary, our findings provide evidence for LINC00460 as a
potential therapeutic target in GC.
Keywords: LINC00460, KDM2A, miR-342-3p, gastric cancer