108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

由氧化应激诱导的 H19 通过激活 NF-κB 信号传导赋予人神经胶质瘤细胞的替莫唑胺耐药性
Authors Duan S, Li M, Wang Z, Wang L, Liu Y
Received 6 May 2018
Accepted for publication 6 July 2018
Published 2 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6395—6404
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S173244
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Background: Recent findings around long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have opened
novel areas of research around their prospective use in overcoming
chemoresistance. Herein, we aimed to investigate the role of lncRNA H19 in
temozolomide (TMZ) resistance of human glioma cells and the possible
mechanisms.
Methods: Short-/long-term oxidative stress was induced, and TMZ-resistant glioma
cells (U251TMZ and
LN229TMZ) were
established. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) and overexpression plasmids were
used to modulate the expression of H19 and/or luciferase the reporters. The MTT
assay and immunoblotting of cleaved caspase-3, cyclin D1, XIAP and Bcl-2 were
conducted to evaluate TMZ sensitivity. Luciferase reporter and quantitative
real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) assays were used to verify the activation of NF-κB
pathways by H19.
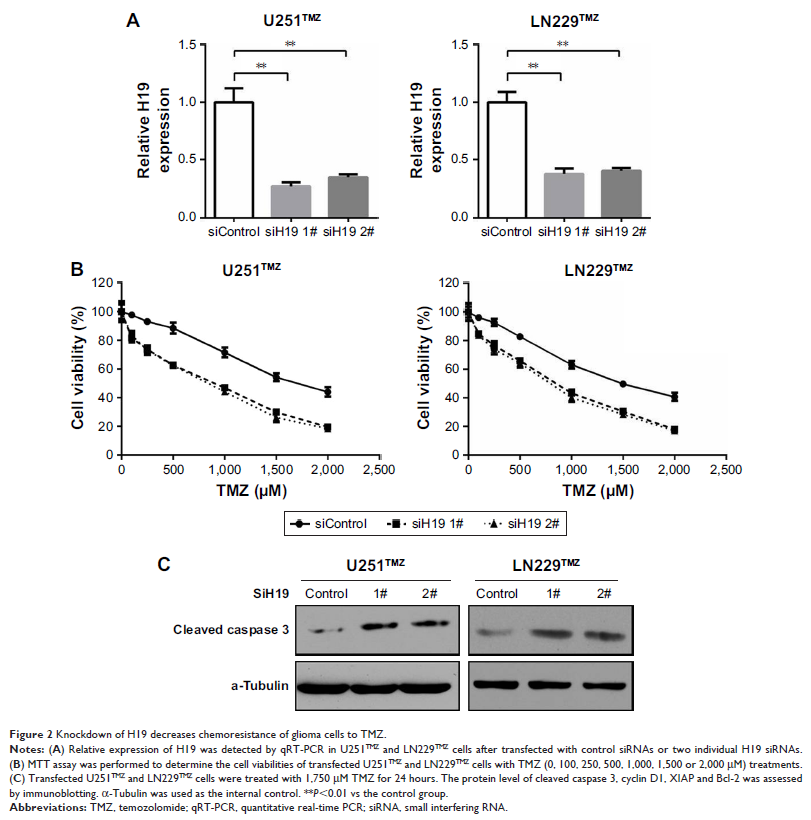
Results: Knockdown of H19 in U251TMZ and LN229TMZ cells decreased half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values for TMZ and increased cell apoptosis, and H19 overexpression in
U251 and LN229 cells led to the opposite effects, indicating that the H19
confers TMZ resistance to glioma cells. Furthermore, knockdown of H19 decreased
the NF-κB signaling, which was revealed by repressed reporter activity and
declined expression of its downstream targets in TMZ-resistant glioma cells. In
contrast, H19 overexpression in U251 and LN229 cells resulted in an increase in
NF-κB activation. Blockage of NF-κB activation by its inhibitor abolished TMZ
resistance caused by H19 overexpression. Addition of H2O2 to induce
oxidative stress largely reversed TMZ sensitivity caused by H19 knockdown.
Conclusion: H19 confers TMZ resistance through activating NF-κB signaling and
may represent a novel therapeutic target for TMZ-resistant gliomas.
Keywords: H19, oxidative stress, TMZ resistance, NF-κB pathway, glioma